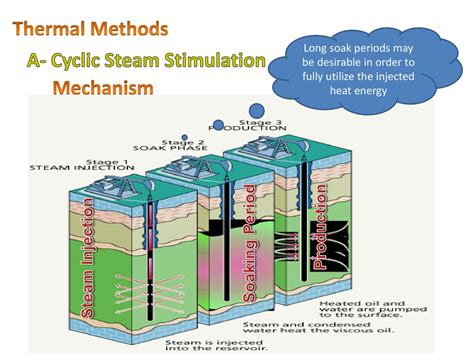
Enhancing oil recovery through cyclic steam stimulation (CSS) is a complex process that requires careful planning, execution, and monitoring. CSS involves injecting steam into a well, allowing it to soak, and then producing the well to extract oil that has been heated and made more viscous by the steam. This process can be repeated multiple times to maximize oil recovery. Here are 12+ cyclic steam stimulation tips for enhanced recovery, designed to help operators optimize their CSS operations and increase the efficiency of their oil recovery efforts.
1. Understanding Reservoir Properties
Before initiating a CSS project, it’s crucial to have a deep understanding of the reservoir properties. This includes the permeability, porosity, oil saturation, and thermal properties of the rock. Advanced logging techniques and core analysis can provide valuable insights into the reservoir’s characteristics, helping to design a more effective CSS strategy.
2. Optimizing Steam Quality and Rate
The quality and rate of steam injection can significantly impact the effectiveness of CSS. Higher quality steam (with lower liquid content) and an optimal injection rate can help to help maximize the heated zone around the wellbore, improving oil mobility and recovery. Advanced steam generators and precise control systems can help achieve these optimal conditions.
3. Wellbore and Completion Design
The design of the wellbore and completion is critical for successful CSS operations. This includes selecting materials that can withstand high temperatures and pressures, designing an efficient steam injection system, and ensuring that the well completion allows for easy and effective steam distribution and oil production.
4. Soak Time and Cycle Optimization
The soak time, which is the period the steam is left to heat the reservoir before production commences, and the number of cycles can significantly affect oil recovery. Balancing these parameters based on reservoir response, steam availability, and production capabilities can optimize the recovery process. Advanced modeling and monitoring can help in making informed decisions about soak times and cycle frequencies.
5. Monitoring and Surveillance
Continuous monitoring of the CSS process is vital. This includes tracking temperature profiles in the well and surrounding reservoir, monitoring production rates, and analyzing the composition of the produced fluids. Advanced surveillance techniques, such as distributed temperature sensing (DTS) and distributed acoustic sensing (DAS), can provide real-time insights into the steam chamber’s growth and oil production dynamics.
6. Dual Horizontal Wells
Using dual horizontal wells, one for steam injection and another for oil production, can improve the efficiency of CSS operations. This setup allows for better control over the steam chamber, more uniform heating, and potentially higher oil recovery rates compared to traditional vertical wells.
7. Integration with Other EOR Techniques
In some cases, combining CSS with other enhanced oil recovery (EOR) techniques, such as polymer flooding or solvent-based methods, can lead to synergistic effects and further enhance oil recovery. The feasibility of such combinations depends on the specific reservoir characteristics and the stage of depletion.
8. Environmental Considerations
CSS operations require significant amounts of water and energy, primarily for steam generation. Implementing water conservation measures, using alternative energy sources (such as solar or cogeneration), and minimizing waste can help reduce the environmental footprint of CSS projects.
9. Economic Analysis
Conducting thorough economic analyses is essential to ensure that CSS operations are viable. This includes considering the costs of steam generation, well maintenance, and potential increases in oil production. The economics of CSS can be highly dependent on oil prices, making continuous monitoring of market trends crucial.
10. Technological Innovation
Staying abreast of technological innovations in steam generation, well completion, and monitoring can offer opportunities to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of CSS operations. Advances in materials science, digitalization, and data analytics can play significant roles in optimizing CSS processes.
11. Operational Flexibility
Maintaining operational flexibility is key to adapting CSS strategies as more data becomes available from the field. This may involve adjusting steam injection rates, modifying well completions, or altering production schedules in response to observed reservoir behavior.
12. Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing
Finally, collaboration among operators, service companies, and research institutions is vital for advancing the practice of CSS. Sharing experiences, challenges, and innovations can help in developing best practices and improving the overall efficiency of CSS operations worldwide.
Additional Considerations
- Reservoir Modeling: Advanced reservoir modeling can help predict the behavior of the reservoir under CSS, aiding in the optimization of the process.
- Artificial Lift Systems: Implementing efficient artificial lift systems can help manage the increased fluid volumes and viscosities associated with CSS, ensuring sustained production rates.
- Well Integrity: Ensuring well integrity throughout CSS operations is critical. This involves careful well design, regular maintenance, and monitoring for any signs of well failure or degradation.
In conclusion, cyclic steam stimulation is a powerful technique for enhancing oil recovery, especially in heavy oil reservoirs. By carefully considering reservoir properties, optimizing steam injection, designing efficient well completions, and continuously monitoring and adapting to the reservoir’s response, operators can maximize the effectiveness of CSS operations. As the oil industry continues to evolve, incorporating technological innovations, environmental considerations, and collaborative knowledge sharing will be essential for the long-term success of CSS and other EOR methods.
What is the primary goal of cyclic steam stimulation (CSS) in oil recovery?
+The primary goal of CSS is to increase the mobility of heavy oil by heating it with steam, making it easier to extract and thus enhancing oil recovery from the reservoir.
How often can the CSS cycle be repeated?
+The CSS cycle can be repeated multiple times, depending on the reservoir’s response and the economics of the operation. Each cycle’s effectiveness may decrease over time as the easily recoverable oil is depleted.
What role does reservoir characterization play in CSS operations?
+Reservoir characterization is crucial for understanding the properties of the oil reservoir, including its permeability, porosity, and oil saturation. This information helps in designing an effective CSS strategy that maximizes oil recovery.