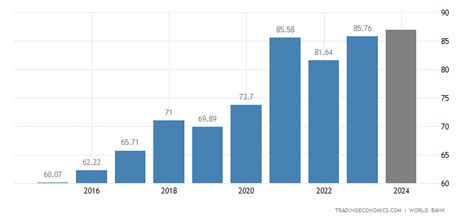
The Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, with its highly developed economy and strategic location in the heart of Europe, has consistently demonstrated remarkable resilience and adaptability in the face of global economic challenges. One of the key indicators of a country’s economic health is its Gross Domestic Product (GDP), which encompasses the total value of all finished goods and services produced within a country’s borders over a specific period. As of the latest available data, Luxembourg’s GDP has shown notable trends that reflect both its strengths and its vulnerabilities to international economic shifts.
Historical Context of Luxembourg’s Economy
Luxembourg’s economic landscape has been shaped by its historical dependence on the steel industry, a sector that once dominated the country’s economy. However, recognizing the need for diversification, the government has successfully implemented policies to attract foreign investment and promote the development of other sectors, most notably financial services, technology, and logistics. This strategic diversification has enabled Luxembourg to maintain a high standard of living and to navigate economic downturns with greater agility than many of its European counterparts.
Current GDP Trends
As of the latest economic reports, Luxembourg’s GDP has continued to grow, albeit at a modest pace. The country’s strong financial sector, coupled with its favorable business environment and highly skilled workforce, has been instrumental in driving this growth. Moreover, Luxembourg has been proactive in embracing innovation, with significant investments in research and development, particularly in the fields of information technology, biotechnology, and renewable energy. These efforts not only bolster the economy but also position Luxembourg as a hub for innovation and sustainability in Europe.
Sectoral Contributions to GDP
The contribution of different sectors to Luxembourg’s GDP is a key indicator of the country’s economic structure and potential for future growth. The financial sector, including banking and insurance, remains a significant contributor to the country’s GDP, reflecting Luxembourg’s status as a major financial hub. However, the technology sector, including IT services and software development, has been gaining ground, driven by the government’s initiatives to foster a startup-friendly ecosystem and attract tech talent from across the globe.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite its strong economic performance, Luxembourg faces several challenges that could impact its future GDP growth. These include the need to maintain competitiveness in the face of rising labor costs, managing the risks associated with a highly financialized economy, and addressing environmental concerns through sustainable practices. On the other hand, opportunities abound, particularly in the areas of digitalization, green economy initiatives, and further diversification of its industrial base. The government’s commitment to investing in education and research infrastructure is expected to yield long-term benefits, enhancing the country’s attractiveness to foreign investors and talent.
International Trade and Investment
Luxembourg’s economy is highly integrated into the global trade system, with a significant portion of its GDP accounted for by exports. The country’s strategic location and its membership in the European Union (EU) facilitate trade with neighboring countries and provide access to a large, integrated market. Furthermore, Luxembourg has been successful in attracting foreign direct investment (FDI), which not only brings in capital but also introduces new technologies, management practices, and market access, further enhancing the country’s economic resilience and competitiveness.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Luxembourg’s GDP reflects the country’s strong economic fundamentals, diversification efforts, and strategic positioning within the European and global economies. While challenges exist, the government’s proactive stance towards innovation, sustainability, and economic diversification bodes well for the country’s future economic growth and stability. As the global economic landscape continues to evolve, Luxembourg is poised to leverage its strengths and adapt to new opportunities, ensuring its continued prosperity and high standard of living.
FAQ Section
What are the main contributors to Luxembourg's GDP?
+The financial sector, including banking and insurance, and the technology sector, including IT services and software development, are among the main contributors to Luxembourg's GDP.
How does Luxembourg's economy benefit from its EU membership?
+Luxembourg's membership in the EU provides it with access to a large, integrated market, facilitating trade with neighboring countries and attracting foreign investment.
What initiatives is the government taking to promote economic diversification and innovation?
+The government is investing in education and research infrastructure, promoting a startup-friendly ecosystem, and attracting tech talent to foster innovation and diversification, particularly in the areas of digitalization and green economy initiatives.
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, Luxembourg’s economic future appears promising, with opportunities for growth in emerging sectors and through continued investment in innovation and sustainability. The country’s ability to adapt to changing global economic conditions, coupled with its strong fundamentals and favorable business environment, positions it well to maintain its economic resilience and competitiveness. As the global economy navigates the challenges of the 21st century, Luxembourg is poised to remain a beacon of stability and prosperity, offering a unique blend of tradition and innovation that continues to attract investors, talent, and businesses from around the world.