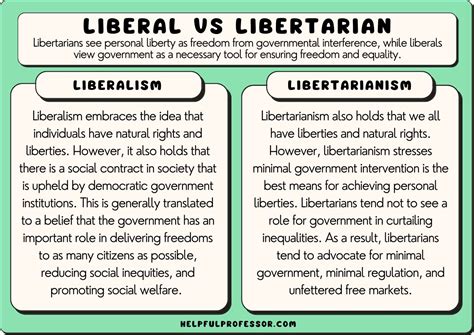
The terms “liberal” and “libertarian” are often misunderstood or used interchangeably, despite referring to distinct philosophical and political ideologies. To clarify the differences between these two concepts, it’s essential to delve into their historical contexts, core principles, and modern interpretations.
Historically, liberalism emerged as a response to the absolute power of monarchies and the church, advocating for individual rights, democracy, and the rule of law. Over time, liberalism has branched out into various forms, including classical liberalism, which emphasizes free markets and minimal government intervention, and modern liberalism, which supports a more active role for government in promoting social welfare and regulating the economy.
Libertarianism, on the other hand, has its roots in the idea of individual liberty and the limitation of government power. Libertarians advocate for the protection of individual rights, especially property rights, and a drastic reduction in government intervention in both personal and economic matters. The core principle of libertarianism is the non-aggression principle, which posits that no individual or group should initiate force against another.
One of the primary differences between liberals and libertarians lies in their views on the role of government. Liberals, particularly modern liberals, see government as a necessary institution for correcting market failures, providing public goods, and ensuring social justice. They believe that government intervention can help mitigate inequalities and protect the rights of marginalized groups. In contrast, libertarians view government with skepticism, arguing that its power should be strictly limited to protecting individual rights and preventing coercion. They advocate for a minimalist state that does not interfere with personal choices or economic activities, except when these infringe upon the rights of others.
Another significant area of difference is economic policy. Liberals often support a mixed economy with a balance between private enterprise and government regulation, aiming to ensure competition, stability, and fairness. They may also advocate for progressive taxation, social welfare programs, and public services as means to reduce inequality and improve living standards. Libertarians, by contrast, are strong advocates for free market capitalism, opposing government regulation, taxation, and any form of intervention in economic affairs. They believe that markets, when left to operate freely, are more efficient and equitable than any system controlled or heavily influenced by the state.
The concept of social justice is also viewed differently through the lenses of liberalism and libertarianism. Liberals tend to emphasize the importance of social and economic equality, advocating for policies that promote equal opportunities and outcomes. They support affirmative action, labor unions, and social welfare programs as tools to combat discrimination and inequality. Libertarians, while also committed to the principle of equality before the law, focus more on the protection of individual rights and freedoms. They argue that true equality can only be achieved through the protection of property rights, freedom of contract, and the elimination of coercive government practices that favor certain groups over others.
In practice, these philosophical differences translate into distinct policy positions. For example, liberals might support universal healthcare as a means to ensure that all citizens have access to necessary medical care, regardless of their economic situation. Libertarians, on the other hand, would likely argue that healthcare should be provided through private markets, with government’s role limited to protecting individual rights and preventing fraud.
The future of both liberal and libertarian ideologies is intertwined with the evolving challenges of the modern world. As societies grapple with issues like climate change, technological disruption, and global inequality, both philosophies must adapt to remain relevant. Liberals face the challenge of reconciling their commitment to social welfare and government intervention with the need for efficient and sustainable solutions to global problems. Libertarians, meanwhile, must confront the limitations of relying solely on market mechanisms to address complex social and environmental issues.
In conclusion, while both liberalism and libertarianism share a commitment to individual liberty and the protection of rights, they diverge significantly in their views on the role of government, economic policy, and social justice. Understanding these differences is crucial for navigating the complex landscape of modern political discourse and for developing informed opinions on the most pressing issues of our time.
Comparative Analysis of Liberal and Libertarian Ideologies
| Ideology | View on Government | Economic Policy | Social Justice |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liberalism | Supports a active role for government in promoting social welfare and regulating the economy. | Mixed economy with government regulation and social welfare programs. | Emphasizes social and economic equality through government intervention. |
| Libertarianism | Advocates for a minimalist state with limited government intervention. | Free market capitalism with minimal regulation and taxation. | Focuses on protecting individual rights and freedoms as the path to true equality. |

Historical Evolution of Liberal and Libertarian Thought
The historical evolution of liberal and libertarian thought reflects changing societal values, technological advancements, and political realities. From the Enlightenment thinkers who first articulated the principles of individual liberty and limited government, to the modern advocates of social liberalism and libertarianism, these ideologies have adapted to the challenges of their times. Understanding this historical context is essential for appreciating the nuances of contemporary liberal and libertarian debates.
Future Trends Projection
As we look to the future, both liberal and libertarian ideologies will face challenges from emerging trends such as the rise of digital technologies, increasing global interconnectedness, and the growing awareness of environmental issues. Liberals will need to balance their commitment to social welfare with the demands of sustainability and technological innovation. Libertarians, meanwhile, will be pressed to demonstrate how free market principles can effectively address global challenges without relying on government intervention. The adaptability and resilience of these ideologies in the face of such challenges will determine their relevance and influence in shaping the future of political and economic systems.
Decision Framework for Choosing Between Liberal and Libertarian Policies
When evaluating the merits of liberal versus libertarian policies, several key factors should be considered:
- Role of Government: What role should government play in addressing social and economic issues?
- Economic Efficiency: How can economic activities be organized to maximize efficiency and innovation?
- Social Justice: What strategies are most effective for promoting equality and fairness in society?
- Individual Rights: How can individual rights and freedoms be best protected and advanced?
- Global Challenges: How can national policies address global issues such as climate change, technological disruption, and economic inequality?
By considering these factors and weighing the arguments presented by both liberal and libertarian perspectives, individuals can develop a well-informed stance on the most appropriate balance between government intervention, individual liberty, and social welfare.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between liberalism and libertarianism?
+The main difference lies in their views on the role of government. Liberals support a more active government role in social welfare and economic regulation, while libertarians advocate for minimal government intervention in personal and economic matters.
Do libertarians support social welfare programs?
+Libertarians generally oppose government-funded social welfare programs, believing that private charity and voluntary associations are more efficient and morally justifiable means of addressing poverty and inequality.
How do liberals view economic policy?
+Liberals often support a mixed economy with a balance between private enterprise and government regulation, aiming to ensure competition, stability, and fairness. They also advocate for progressive taxation and social welfare programs to reduce inequality.
What is the non-aggression principle in libertarianism?
+The non-aggression principle is a core tenet of libertarianism, stating that no individual or group should initiate force against another. This principle guides libertarian views on issues ranging from personal freedom to foreign policy.
Can one be both liberal and libertarian?
+While the two ideologies have distinct differences, individuals may identify with aspects of both. Classical liberals, for instance, share some similarities with libertarians in their support for free markets and limited government. However, modern liberalism’s emphasis on social welfare and government regulation typically diverges from libertarian principles.