Bone Cell Drawing
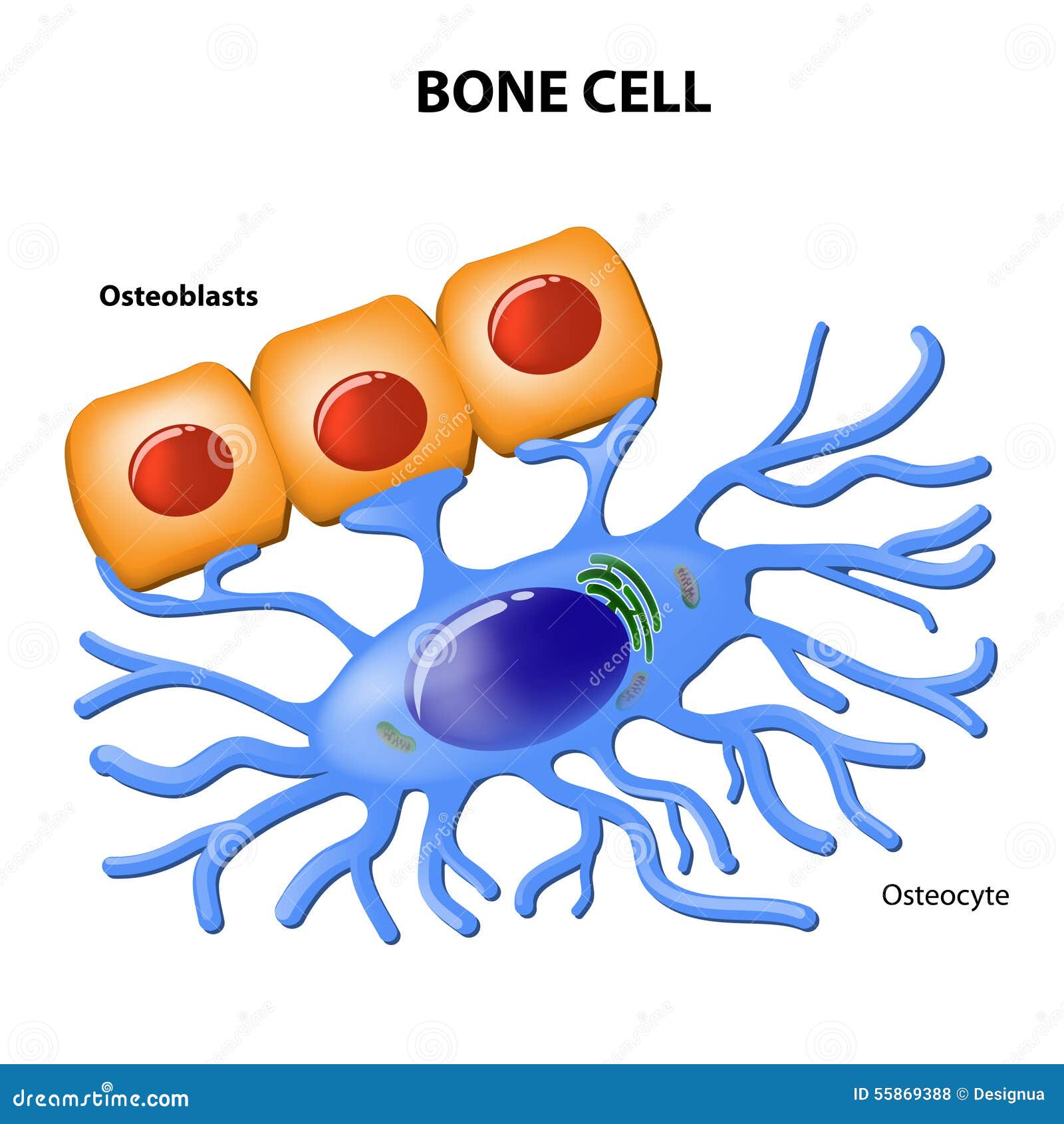
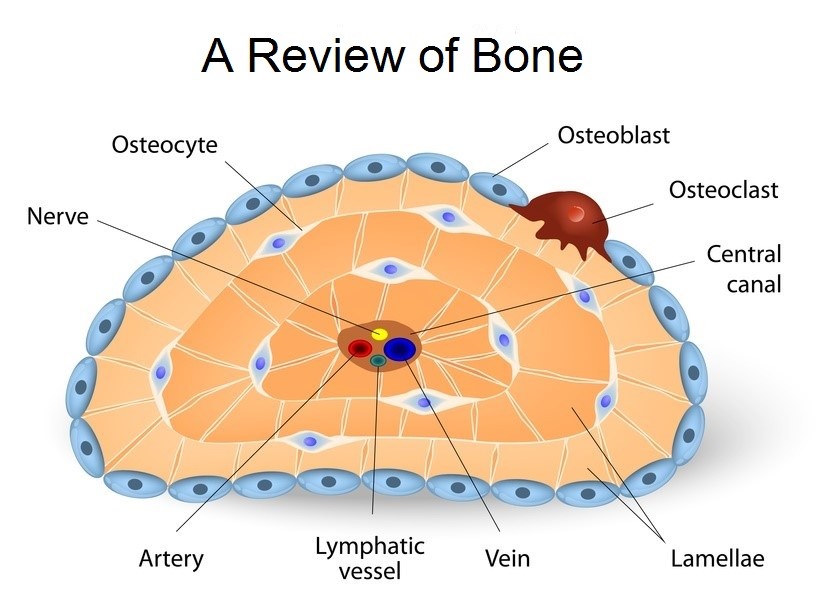
Bone Cell Drawing - The diaphysis is the narrow, tubular shaft that runs between the two bulbous ends of the bone. Osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteogenic cells, and osteoclasts (figure 6.\(\pageindex{5}\)). Four types of cells are found within bone tissue: Osteoprogenitor cells are the 'stem' cells of bone, and are the source of new osteoblasts. It occupies a small chamber called a lacuna, which is contained in the calcified matrix of bone.
Introduction bone is a mineralized connective tissue that exhibits four types of cells: Small channels ( canaliculi) radiate from the lacunae to the osteonic (haversian) canal to provide passageways through the hard matrix. Web a diagram of the human skeleton showing bone and cartilage. View, isolate, and learn human anatomy structures with zygote body. These organs, the function of which involves motion, expansion, and contraction, must have a flexible and elastic protective. The most robust aspect of this unit is the underlying bony architecture. The different types of bone cells include the following:
Human bone cells anatomy stock vector. Illustration of biological
Web click to view large image. The skeletal system includes all of the bones and joints in the body. Identify the anatomical features of a bone define and list examples of bone markings describe the histology of bone tissue compare and contrast compact and spongy bone identify the structures that compose compact and spongy bone.
Bone cells stock vector. Illustration of health, osteon 55869388
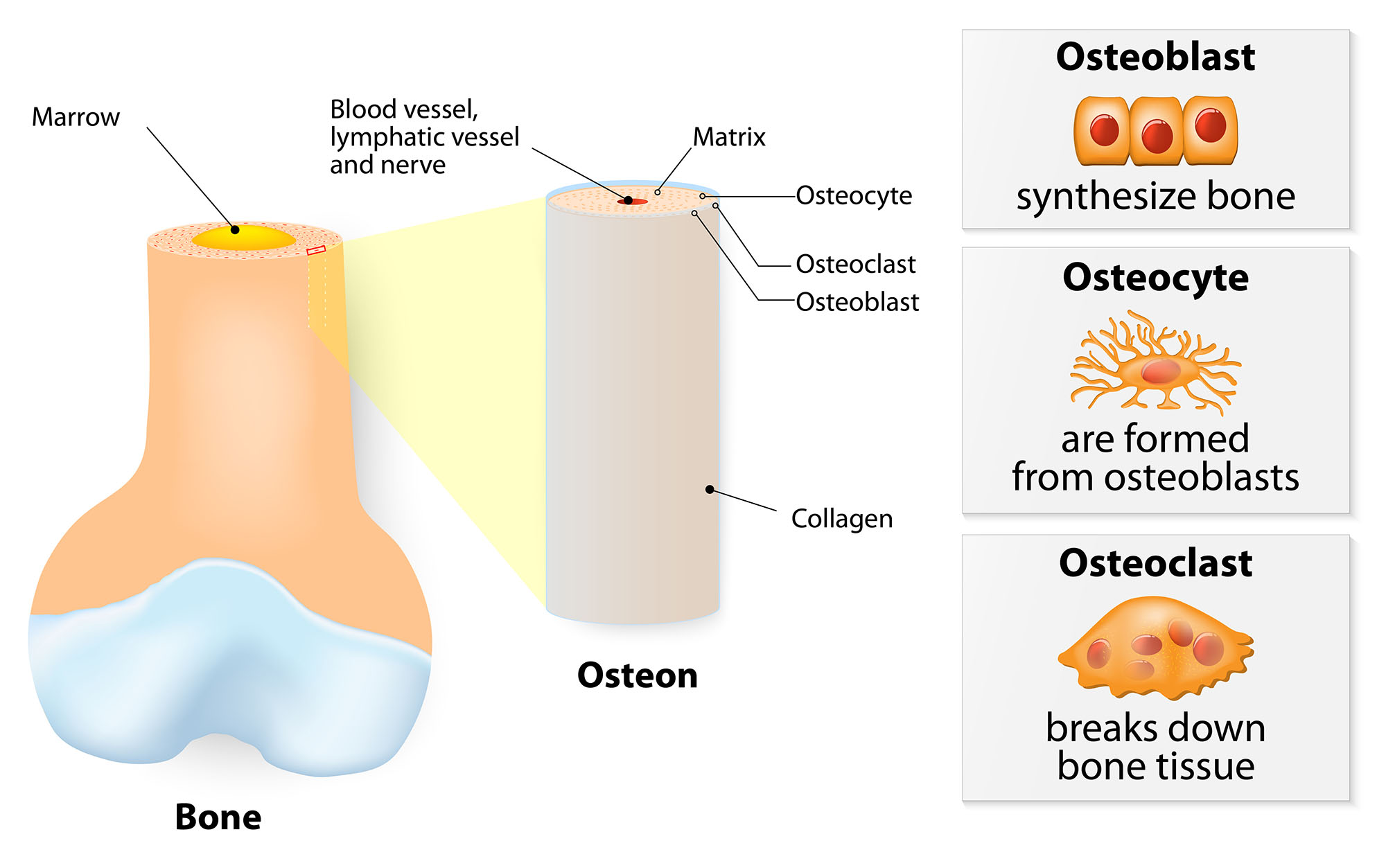
Osteoblasts , lining the surface of bone, secrete collagen and the organic matrix of bone (osteoid), which becomes calcified soon after it has been deposited. Cell see all related content → osteocyte, a cell that lies within the substance of fully formed bone. The diaphysis, two metaphyses, and two epiphyses. Science & tech related topics:.
Human bone cells anatomy Royalty Free Vector Image
Osteoblasts , lining the surface of bone, secrete collagen and the organic matrix of bone (osteoid), which becomes calcified soon after it has been deposited. It occupies a small chamber called a lacuna, which is contained in the calcified matrix of bone. The skeletal system includes all of the bones and joints in the body..
2a3 Bone Structure HumanBio
The skeleton acts as a scaffold by providing support and protection for the soft tissues that make up the rest of the body. Bone exerts important functions in the body, such as locomotion, support and protection of soft tissues, calcium and phosphate storage, and harboring of bone marrow [ 3, 4 ]. Cortical bone, substantia.
Bone Cell Structure And Function
The skeleton acts as a scaffold by providing support and protection for the soft tissues that make up the rest of the body. A long bone has five zones: View, isolate, and learn human anatomy structures with zygote body. In this review, we discuss the current data about the structure and functions of bone cells.
2a3 Bone Structure HumanBio
Introduction bone is a mineralized connective tissue that exhibits four types of cells: Osteoblasts, osteoclasts, osteocytes, and osteoprogenitor (or osteogenic) cells. Science & tech related topics: Web the structure of a long bone allows for the best visualization of all of the parts of a bone (figure 5.3.1 5.3. Osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteogenic cells, and osteoclasts.
Bone Doctor Osteocytes Louisville Orthopedic Surgeon
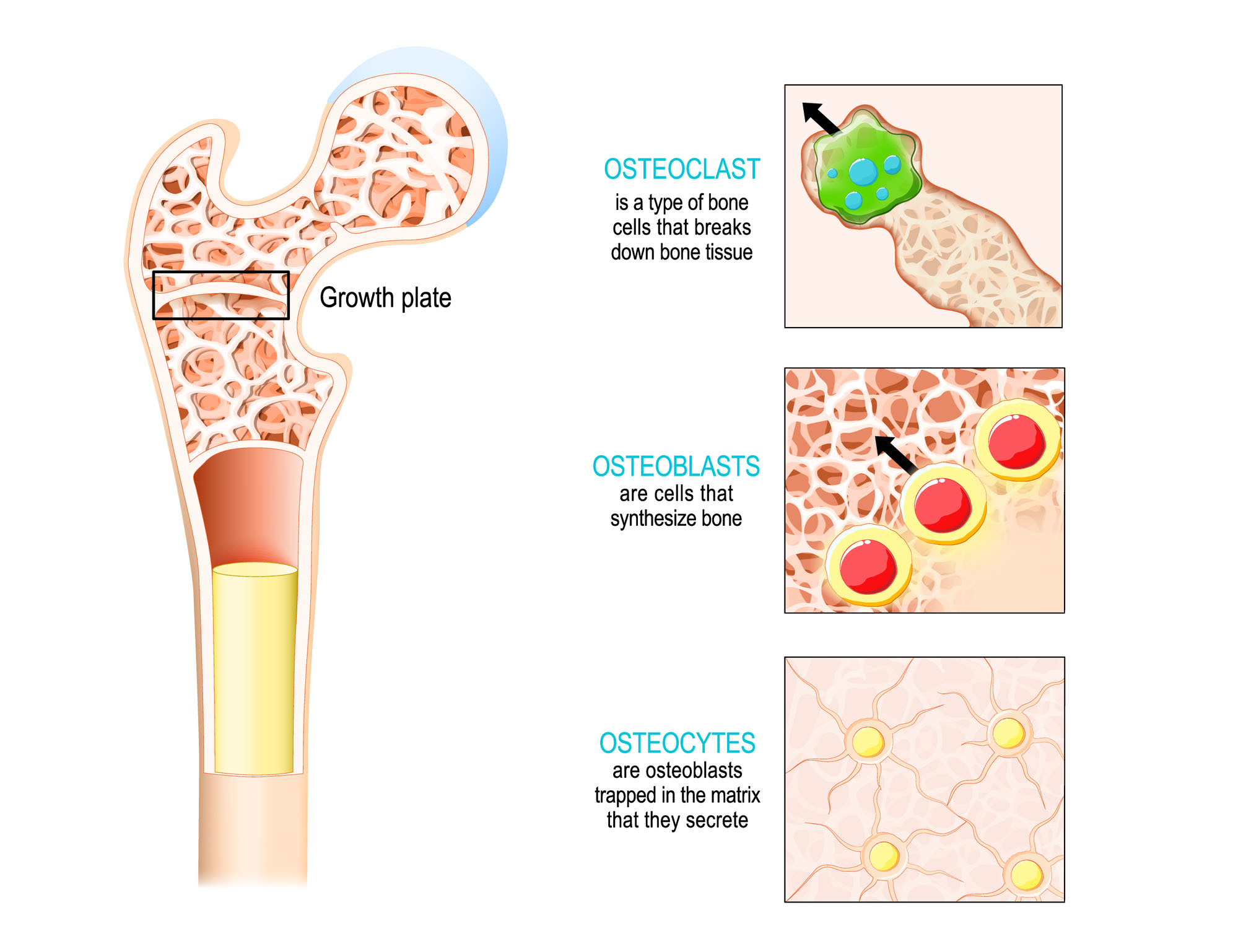
A long bone has five zones: Web although bone cells compose a small amount of the bone volume, they are crucial to the. The osteoblast, the bone cell responsible for forming new bone, is found in the growing portions of bone, including the periosteum and endosteum. Osteogenic cells are undifferentiated and develop into osteoblasts. Web.
Human bone cell types vector illustration infographic Osteoblast
Introduction bone is a mineralized connective tissue that exhibits four types of cells: Web a diagram of the human skeleton showing bone and cartilage. Web cells that are involved in growing bone: Protection of the heart, lungs, and other organs and structures in the chest creates a problem somewhat different from that of the central.
Human bone cells anatomy Royalty Free Vector Image
The skeleton acts as a scaffold by providing support and protection for the soft tissues that make up the rest of the body. The most robust aspect of this unit is the underlying bony architecture. Cortical bone, substantia compacta the strength, shape and stability of the human body are dependent on the musculoskeletal system. Introduction.
Bone cells human anatomy organs
Web the three main types of cells that make up bone tissue include: Web is a type of connective tissue consisting mainly of a collagen matrix that is mineralized with calcium and phosphorus crystals. The skeletal system includes all of the bones and joints in the body. Osteoblasts , lining the surface of bone, secrete.
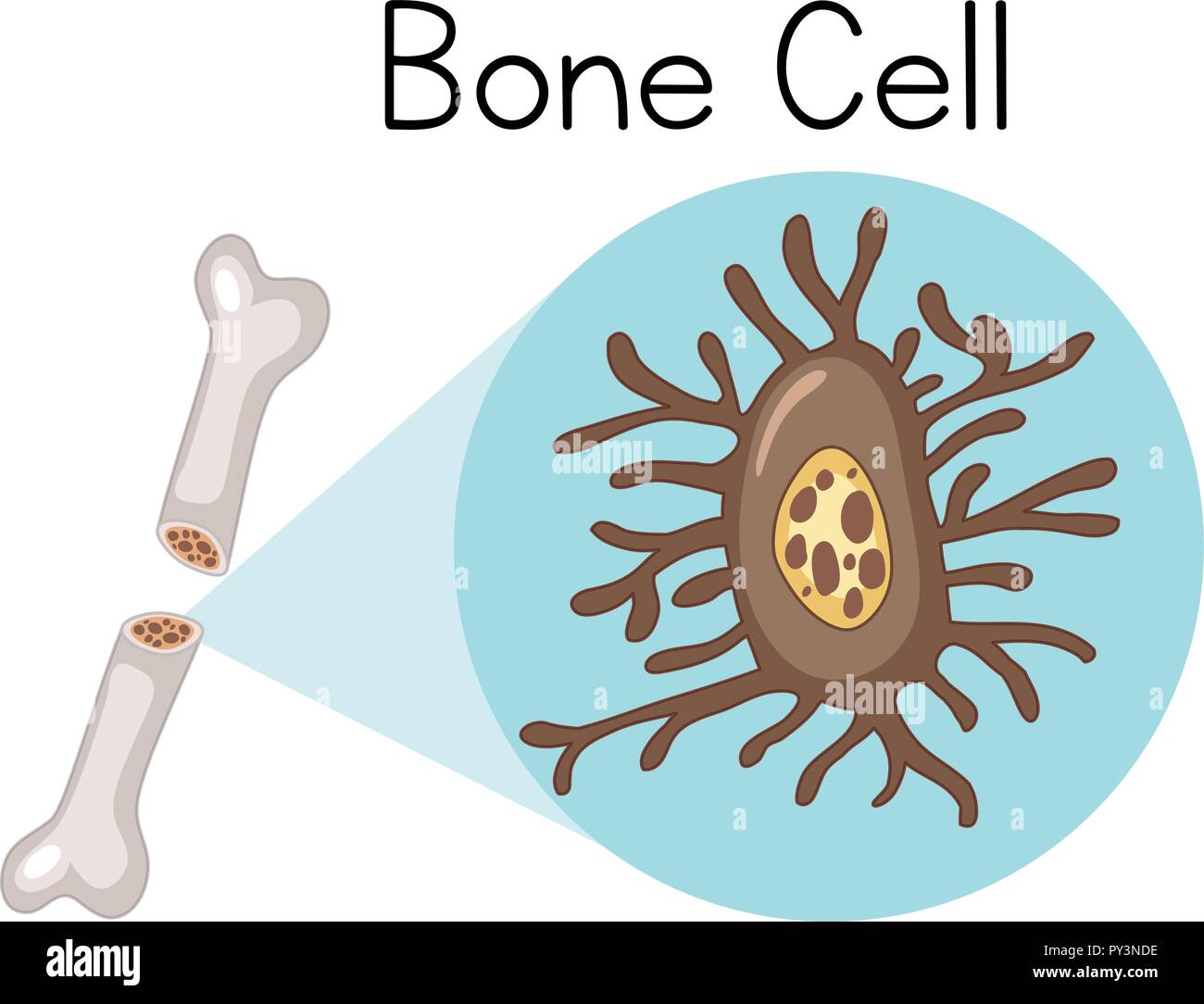
Bone Cell Drawing Web between the rings of matrix, the bone cells (osteocytes) are located in spaces called lacunae. Web although bone cells compose a small amount of the bone volume, they are crucial to the. A long bone has five zones: These organs, the function of which involves motion, expansion, and contraction, must have a flexible and elastic protective. Bone tissue is made up of four different types of bone cells;
Web Skeletal System Diagram Special Sense Organs Urinary System Diagram Cancer Cardiology Cpr Diagram Dentistry Diabetes Diseases Disorders
Web four types of cells are found within bone tissue. Osteoblasts , lining the surface of bone, secrete collagen and the organic matrix of bone (osteoid), which becomes calcified soon after it has been deposited. These organs, the function of which involves motion, expansion, and contraction, must have a flexible and elastic protective. The skeleton acts as a scaffold by providing support and protection for the soft tissues that make up the rest of the body.
Web The Structure Of A Long Bone Allows For The Best Visualization Of All Of The Parts Of A Bone (Figure 5.3.1 5.3.
The diaphysis is the narrow, tubular shaft that runs between the two bulbous ends of the bone. Bone anatomy there are several different types of tissues in bones, including two types of osseous tissues. It occupies a small chamber called a lacuna, which is contained in the calcified matrix of bone. Web there are three types of bone cells present in human body:
The Skeletal System Includes All Of The Bones And Joints In The Body.
Web cells that are involved in growing bone: Bone is a modified form of connective tissue which is made of extracellular matrix, cells and fibers. Cortical bone, substantia compacta the strength, shape and stability of the human body are dependent on the musculoskeletal system. Web bone consists of four types of cells:
The Most Robust Aspect Of This Unit Is The Underlying Bony Architecture.
Each cell type has a unique function and is found in different locations in bones. Osteoblasts, osteoclasts, osteocytes, and osteoprogenitor (or osteogenic) cells. Osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteogenic cells, and osteoclasts (figure 6.\(\pageindex{5}\)). Web what are the different types of bone cells?