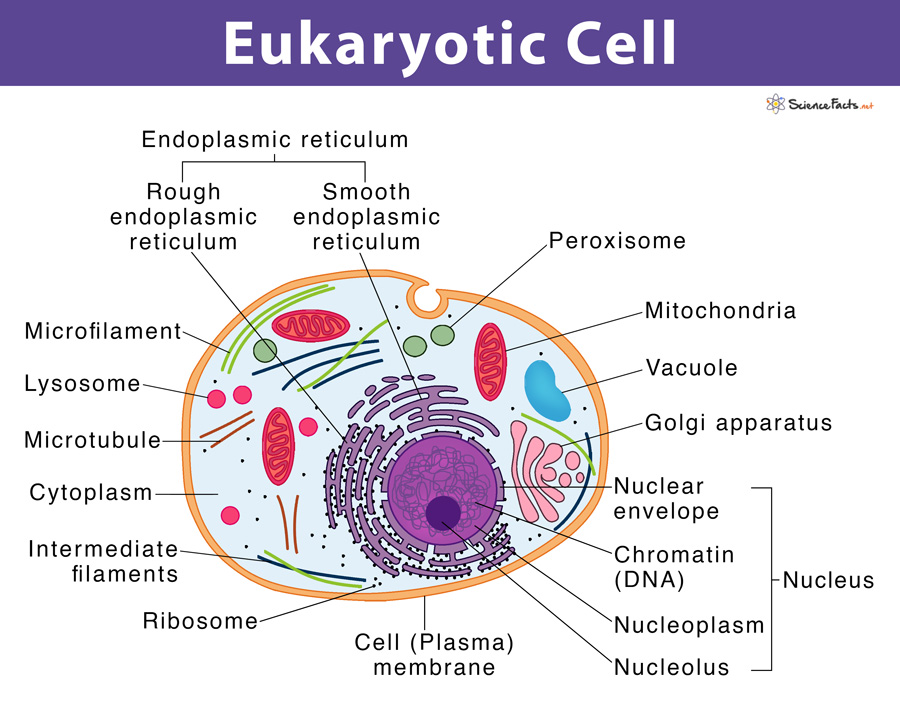
Draw A Eukaryotic Cell
Draw A Eukaryotic Cell - Web unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: Web the division cycle of most eukaryotic cells is divided into four discrete phases: Mitochondria are where atp is made. Organisms with eukaryotic cells are called eukaryotes, and they range from fungi to people. Web a eukaryotic cell is one of two different types of cells.
It is absent in animal cells and some protists. Web a eukaryotic cell is one of two different types of cells. Organisms with eukaryotic cells are called eukaryotes, and they range from fungi to people. Web what exactly are eukaryotic cells? The nucleus separates the genetic blueprint, i.e., dna from the cell cytoplasm. The rest of our discussion will strictly be on eukaryotes. Organisms that are based on the eukaryotic cell are called “eukaryotes” and include plants, animals, fungi, and protists.
Biology Club Our cells 1 ( structure, function, division, disorder
During the mitotic (m) phase, the cell separates its dna into two sets and divides its cytoplasm, forming two new cells. Also identifying the difference between the plant and animal cell structure (both eukaryotic cells). Web eukaryotic cells are much more complicated than those of prokaryotes. Eukaryotic cells are defined by the presence of a.
3.4 Unique Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cells Microbiology 201
Prokaryotes are cells that do not have membrane bound nuclei, whereas eukaryotes do. They're also the more complex of the two. During the mitotic (m) phase, the cell separates its dna into two sets and divides its cytoplasm, forming two new cells. Web characteristics structure diagram cell cycle examples what is a eukaryotic cell? Eukaryotic.
Eukaryotic Cell Definition, Characteristics, Structure and Examples
During the mitotic (m) phase, the cell separates its dna into two sets and divides its cytoplasm, forming two new cells. Web eukaryotic cells are much more complicated than those of prokaryotes. Smallest functional unit within a. Vacuoles are storage compartments that sequester waste and help maintain water balance. M phase (mitosis) is usually followed.
Diagram Of A Eukaryotic Cell Drivenheisenberg
Mitochondria are where atp is made. 2.3.2 annotate the diagram from 2.3.1 with the functions of each named structure. They are packed with a fascinating array of subcellular structures that play important roles in energy balance, metabolism, and gene expression. Web a eukaryote cell is the one which has an organised nucleus and several membrane.
Eukaryote Cell Section Drawing Stock Illustration Illustration of
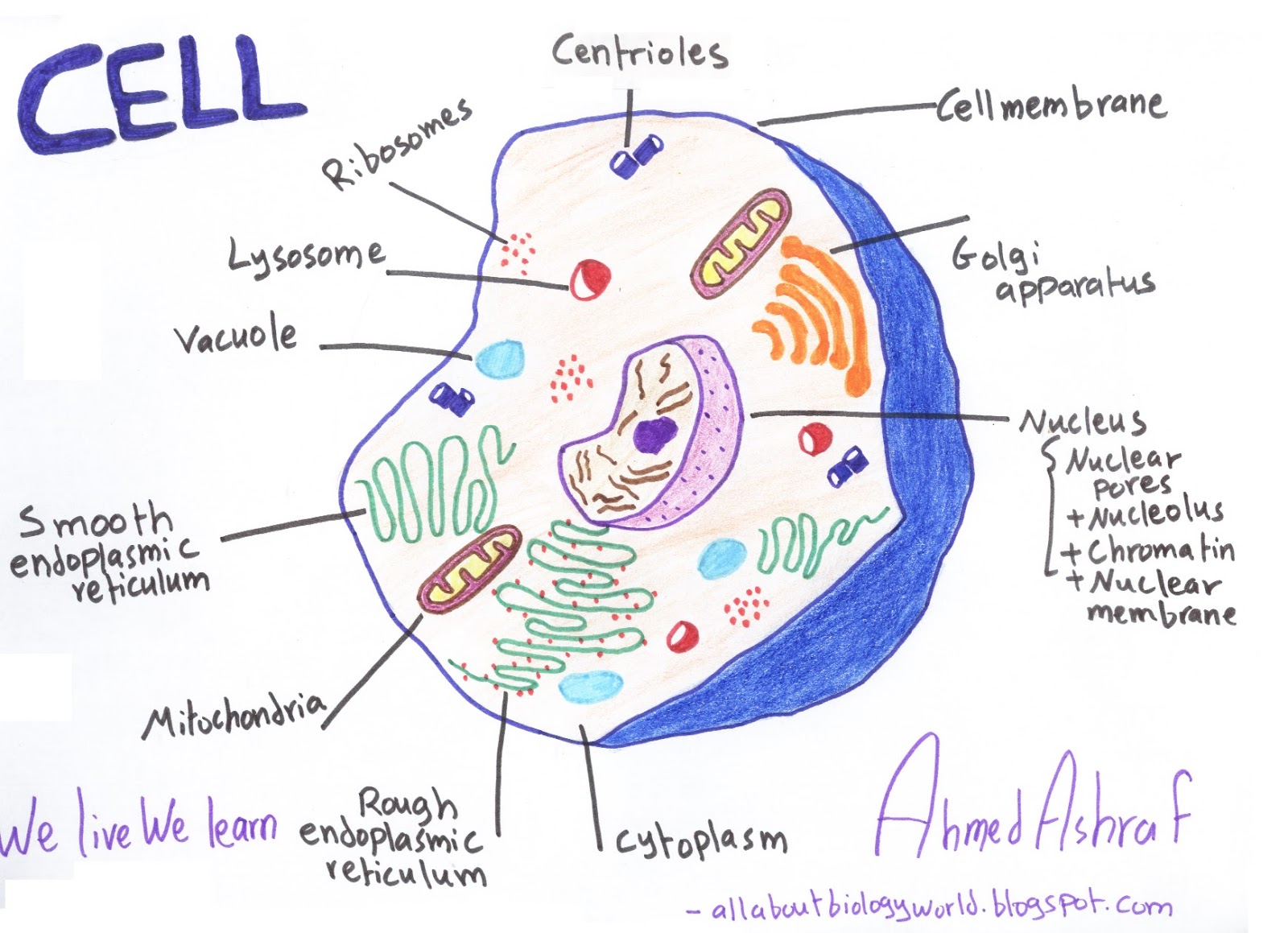
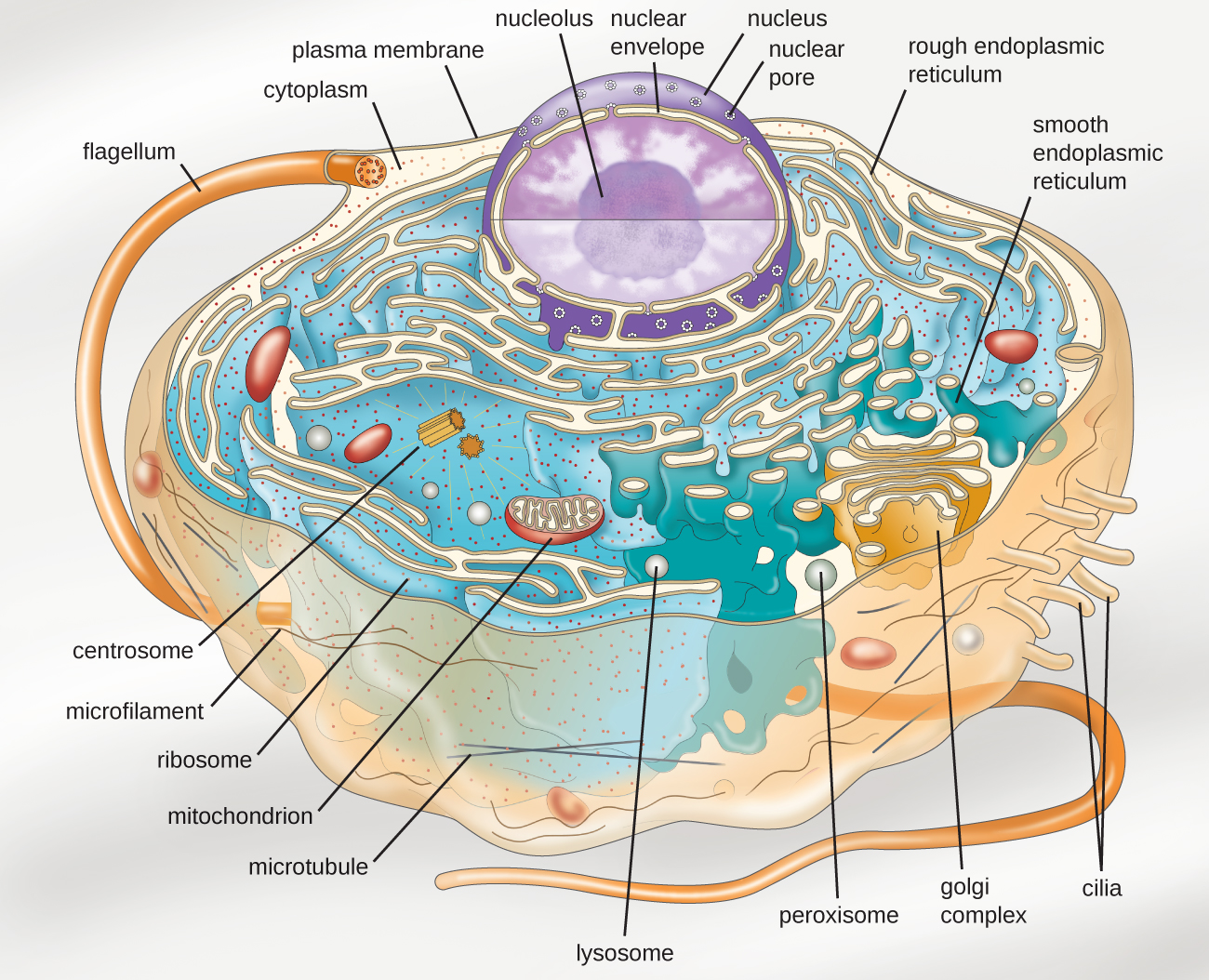
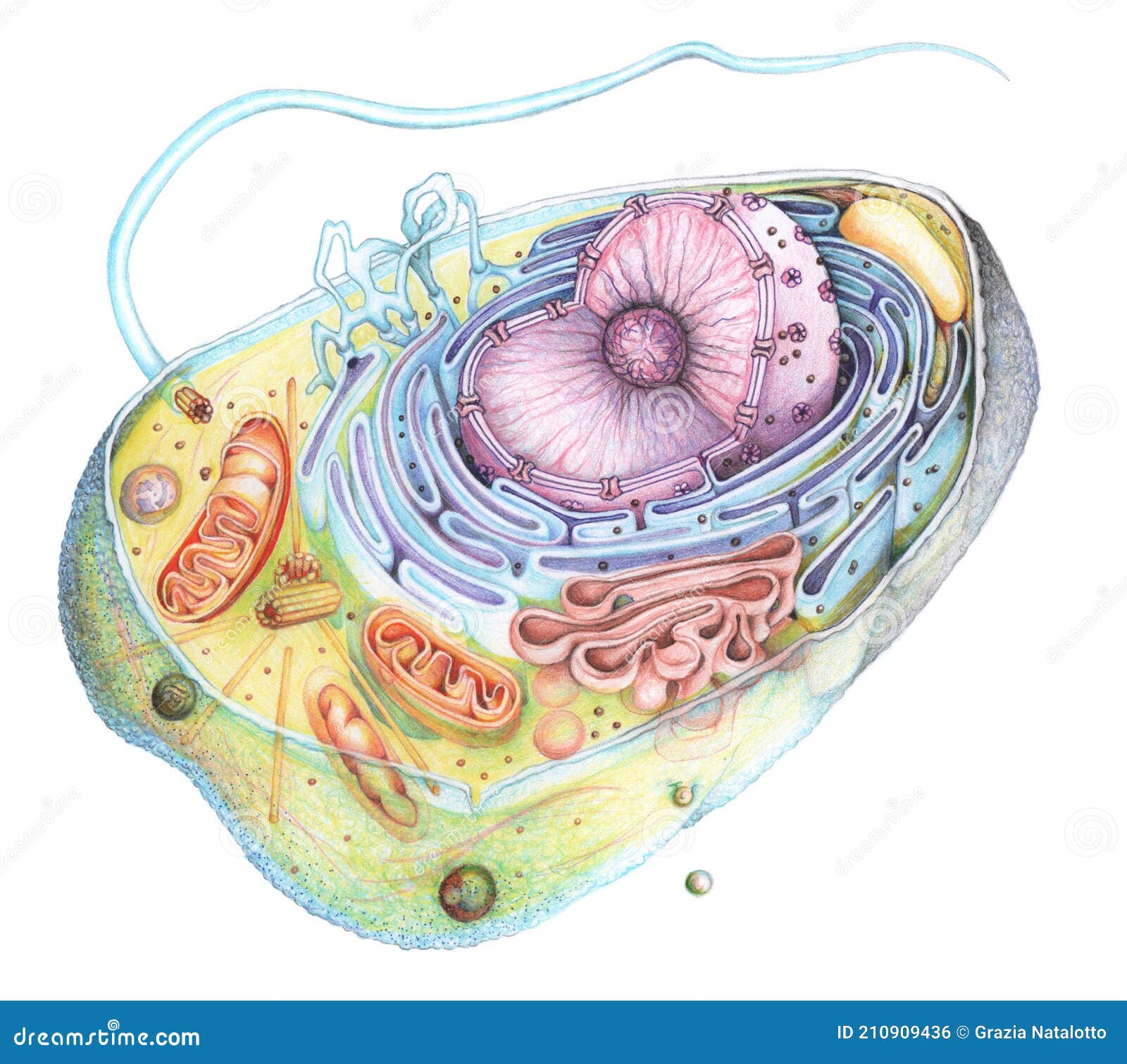
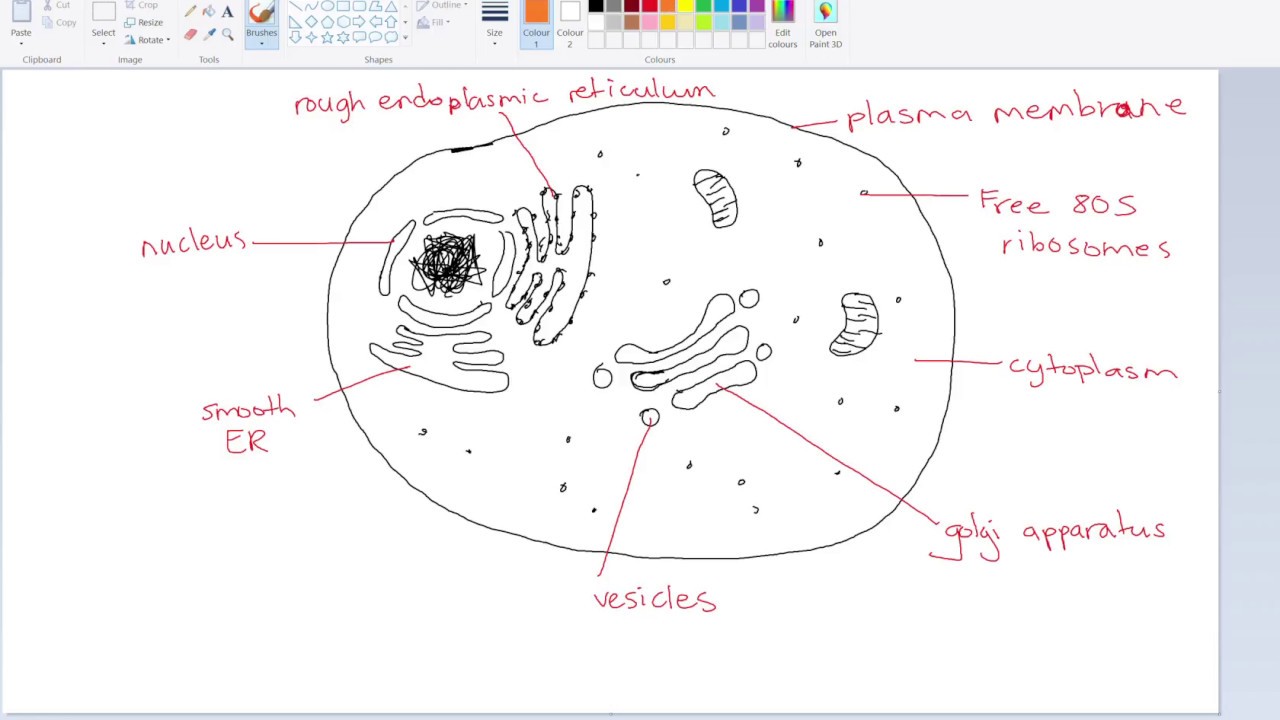
Web eukaryotic cells 2.3.1 draw and label a diagram of the ultrastructure of a liver cell as an example of an animal cell. Although the eukaryotic nucleus breaks down during mitosis and meiosis as chromosomes form and cells divide, it spends most of its time in interphase, the time between cell divisions.this is where the.
How to draw a Eukaryotic Cell IB Biology YouTube
Web key facts about eukaryotic cells; Web a eukaryotic cell is one of two different types of cells. Eukaryotic cells are usually larger than prokaryotic cells, and they are found mainly in multicellular organisms. Also identifying the difference between the plant and animal cell structure (both eukaryotic cells). Web characteristics structure diagram cell cycle examples.
Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cellular Structures ALevel Biology
2.3.2 annotate the diagram from 2.3.1 with the functions of each named structure. Web a eukaryote cell is the one which has an organised nucleus and several membrane covered cell organelles. Think about what a factory needs in order to function effectively. Different cells in a multicellular organism may express very different sets of. Eukaryotic.
Eukaryotic Cell Definition, Structure, & Examples
Cell wall is present in cells of plants, fungi and some protists. Web eukaryotic cells 2.3.1 draw and label a diagram of the ultrastructure of a liver cell as an example of an animal cell. Web key facts about eukaryotic cells; During the mitotic (m) phase, the cell separates its dna into two sets and.
Biology 101 Cells Owlcation
Gene regulation is the process of controlling which genes in a cell's dna are expressed (used to make a functional product such as a protein). Web drawing eukaryotic cells and annotating the functions of each of the organelles. Web unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: The only organisms that are not based on the eukaryotic.
Eukaryotic cell diagram easy How to draw Eukaryotic cell diagram step
Protozoa, fungi, plants, and animals all have eukaryotic cells. Because a membrane surrounds eukaryotic cell’s nucleus, it has a “true. Eukaryotic cells are defined by the presence of a nucleus containing the dna genome and bound by a nuclear membrane (or nuclear envelope) composed of two lipid bilayers that regulate transport of materials into and.
Draw A Eukaryotic Cell The rest of our discussion will strictly be on eukaryotes. Organisms that are based on the eukaryotic cell are called “eukaryotes” and include plants, animals, fungi, and protists. Web the division cycle of most eukaryotic cells is divided into four discrete phases: Web a eukaryotic cell is one of two different types of cells. Web in eukaryotic cells, or cells with a nucleus, the stages of the cell cycle are divided into two major phases:
They Are Classified Under The Kingdom Eukaryota.
Vacuoles are storage compartments that sequester waste and help maintain water balance. It is absent in animal cells and some protists. Protozoa, fungi, plants, and animals all have eukaryotic cells. Cell wall is present in cells of plants, fungi and some protists.
Interphase And The Mitotic (M) Phase.
Organisms that are based on the eukaryotic cell are called “eukaryotes” and include plants, animals, fungi, and protists. Web eukaryotic cells are much more complicated than those of prokaryotes. During the mitotic (m) phase, the cell separates its dna into two sets and divides its cytoplasm, forming two new cells. Web drawing eukaryotic cells and annotating the functions of each of the organelles.
Except Monera, The Cells Of All Other Kingdoms Have Eukaryotic Organisation.
Although the eukaryotic nucleus breaks down during mitosis and meiosis as chromosomes form and cells divide, it spends most of its time in interphase, the time between cell divisions.this is where the status of genes (and therefore of the proteins. The endoplasmic reticulum and golgi body are involved in protein maturation and transport. Think about what a factory needs in order to function effectively. Web characteristics structure diagram cell cycle examples what is a eukaryotic cell?
Web A Eukaryotic Cell Is One Of Two Different Types Of Cells.
Web the division cycle of most eukaryotic cells is divided into four discrete phases: 2.3.2 annotate the diagram from 2.3.1 with the functions of each named structure. Web in eukaryotic cells, or cells with a nucleus, the stages of the cell cycle are divided into two major phases: Web key concepts and summary.