Draw The Orbital Diagram
Draw The Orbital Diagram - This is done by first determining the subshell (s,p,d, or f) then drawing in each electron according to the stated rules above. C) would you expect the bond in cn − to be stronger or weaker than in the f 2 molecule? Construct a molecular orbital diagram of the kind shown in this lesson for a simple diatomic molecule, and indicate whether the molecule or its positive and negative ions should be stable. Web describe the essential difference between a sigma and a pi molecular orbital. Web valence bond theory vbt.
Discover the three rules for creating electron orbital charts, and study examples of filling electron orbital in a diagram. Overlapping atomic orbitals produce molecular orbitals located in the middle of the diagram. The aufbau principle states that electrons occupy atomic orbitals in an ascending energy. These orbitals are filled with electrons (the amount of electrons depends on which element you are looking at). Below are dot density diagrams, boundary surface diagrams, and a rotating image. An orbital diagram, like those shown above, is a visual way to reconstruct the electron configuration by showing each of the separate orbitals and the spins on the electrons. The remaining two electrons occupy the 2p subshell.
Shapes of Atomic Orbitals — Overview & Examples Expii
Web an orbital diagram, or orbital box diagram, is a way of representing the electron configuration of an atom. Web here’s how you can draw the orbital diagram of fluorine step by step. The electron configuration for phosphorus is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3 s 2 3p 3 and the orbital diagram is.
Drawing Orbital Diagrams
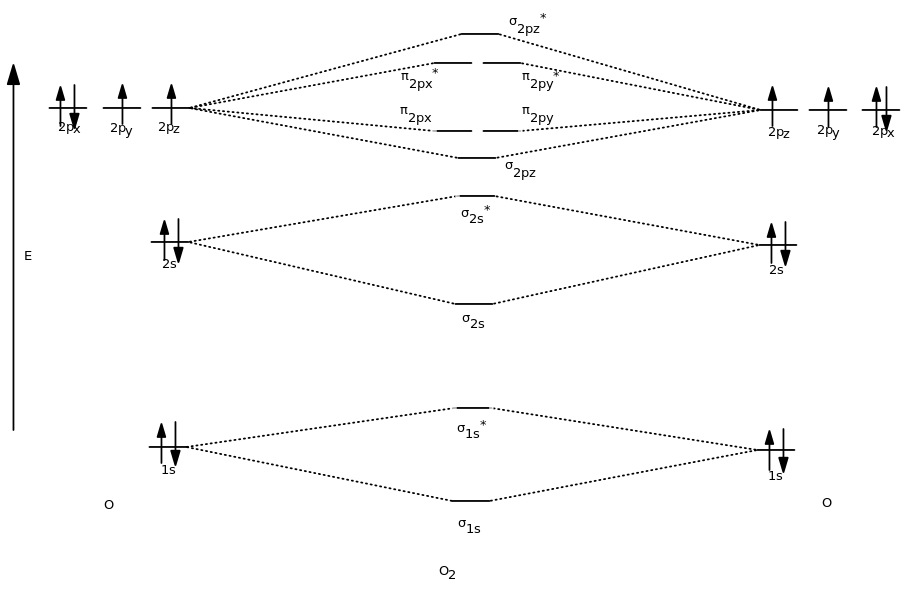
Web describe the essential difference between a sigma and a pi molecular orbital. Individual atomic orbitals (ao) are arranged on the far left and far right of the diagram. Valence bond theory (vbt) in simple terms explains how individual atomic orbitals with an unpaired electron each, come close to each other and overlap to form.
Distribution of Electrons in Different Orbits [with Examples] Teacho
Web this video goes over how to properly draw orbital diagrams for an element, after determining the electron configuration. #2 write electron configuration of fluorine. Orbital diagrams must follow 3 rules: As per hund’s rule, the degenerate atomic orbitals are first singly filled and then pairing occurs. The aufbau principle states that electrons occupy atomic.
Atomic orbitals explained polizhuge
It explains how to write the orbital diagram notation (with arrows) of an element. Web text 5 orbital diagrams orbital diagrams help visualize which orbitals the electrons in an atom are the basics of orbital diagrams there are different types of orbitals, that all have different energy levels. Boundary surface diagrams of the constant probability.
Orbital Diagrams — Overview & Examples Expii
Web atomic orbital diagrams beginning with your selected element, determine the atomic number. A p orbital along the y axis is labeled p y and one along the z axis is a p z orbital. An orbital diagram, like those shown above, is a visual way to reconstruct the electron configuration by showing each of.
Top Notch Tips About How To Draw Orbital Diagrams Spellquestion
(using the aufau principle to order the orbitals and hence the boxes, lines or circles, as shown below) 1s. Web learn how to draw orbital diagrams. Web general notes on molecular orbital diagrams. Web orbital diagrams are pictorial representations of the electron configuration, showing the individual orbitals and the pairing arrangement of electrons. Web when.
Drawing Atomic and Molecular Orbitals Diagrams for Molecules Organic
A box, line, or circle, is drawn to represent each orbital in the electron configuration. You can effortlessly find every single detail about the elements from this single interactive periodic table. Define bond order, and state its significance. Discover the three rules for creating electron orbital charts, and study examples of filling electron orbital in.
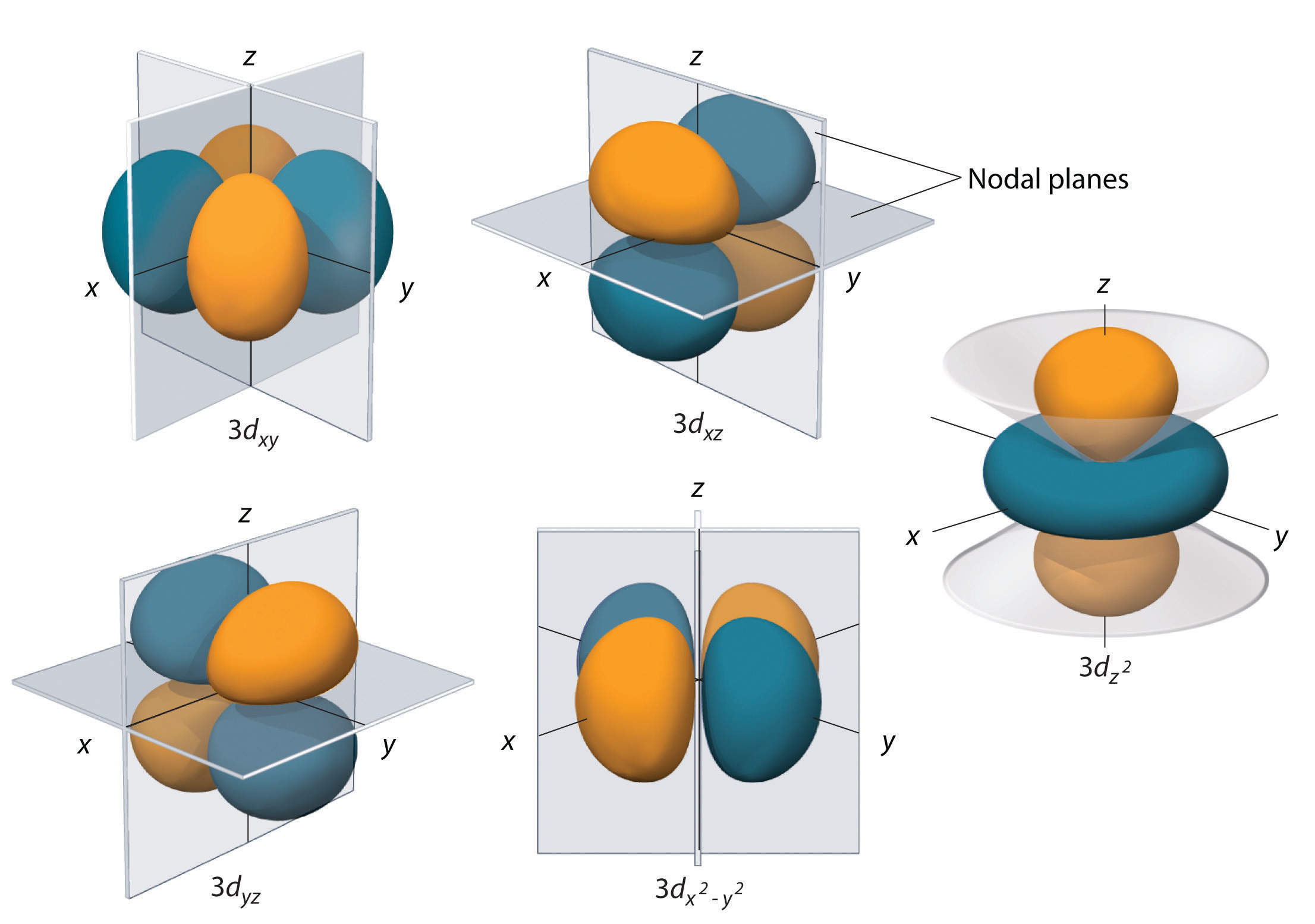
6.6 3D Representation of Orbitals Chemistry LibreTexts
Web this chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into orbital diagrams and electron configuration. Valence bond theory (vbt) in simple terms explains how individual atomic orbitals with an unpaired electron each, come close to each other and overlap to form a molecular orbital giving a covalent bond. Carbon (atomic number 6) has six electrons..
8.3 Development of Quantum Theory CHEM 1114 Introduction to Chemistry
Discover the three rules for creating electron orbital charts, and study examples of filling electron orbital in a diagram. This makes it a challenge to draw, but i will show you the. Orbital diagrams must follow 3 rules: Web orbital diagrams give you all of the information you need about the electron configuration and occupied.
Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified by Megan Lim Medium
A p orbital along the y axis is labeled p y and one along the z axis is a p z orbital. Web valence bond theory vbt. #1 find electrons of fluorine. This is done by first determining the subshell (s,p,d, or f) then drawing in each electron according to the stated rules above. Construct.
Draw The Orbital Diagram You will also get the hd images of the periodic table (for free). #3 draw orbital diagram of fluorine. Once the atomic number has been identified, write the. Web atomic orbital diagrams beginning with your selected element, determine the atomic number. An orbital diagram, like those shown above, is a visual way to reconstruct the electron configuration by showing each of the separate orbitals and the spins on the electrons.
#2 Write Electron Configuration Of Fluorine.
#3 draw orbital diagram of fluorine. Web this video goes over how to properly draw orbital diagrams for an element, after determining the electron configuration. Below are dot density diagrams, boundary surface diagrams, and a rotating image. Discover the three rules for creating electron orbital charts, and study examples of filling electron orbital in a diagram.
It Explains How To Write The Orbital Diagram Notation (With Arrows) Of An Element.
Four of them fill the 1s and 2s orbitals. The electron configuration for phosphorus is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3 s 2 3p 3 and the orbital diagram is drawn below. Let us represent the shapes of orbitals with the help of boundary surface diagrams: Valence bond theory (vbt) in simple terms explains how individual atomic orbitals with an unpaired electron each, come close to each other and overlap to form a molecular orbital giving a covalent bond.
Web Orbital Diagrams Are Pictorial Representations Of The Electron Configuration, Showing The Individual Orbitals And The Pairing Arrangement Of Electrons.
Web a p orbital which extends along the x axis is labeled a p x orbital. The remaining two electrons occupy the 2p subshell. This is done by first determining the subshell (s,p,d, or f) then drawing in each electron according to the stated rules above. The shape of s orbitals
Web Atomic Orbital Diagrams Beginning With Your Selected Element, Determine The Atomic Number.
An orbital diagram, like those shown above, is a visual way to reconstruct the electron configuration by showing each of the separate orbitals and the spins on the electrons. You will get the detailed information about the periodic table which will convert a newbie into pro. Web describe the essential difference between a sigma and a pi molecular orbital. We start with a single hydrogen atom (atomic number 1), which consists of one proton and one electron.



![Distribution of Electrons in Different Orbits [with Examples] Teacho](https://d77da31580fbc8944c00-52b01ccbcfe56047120eec75d9cb2cbd.ssl.cf6.rackcdn.com/00d8e8eb-2904-4147-abf9-6d87a6c24f05/14.-orbits-teachoo-01.png)