Eukaryotic Cell Drawing
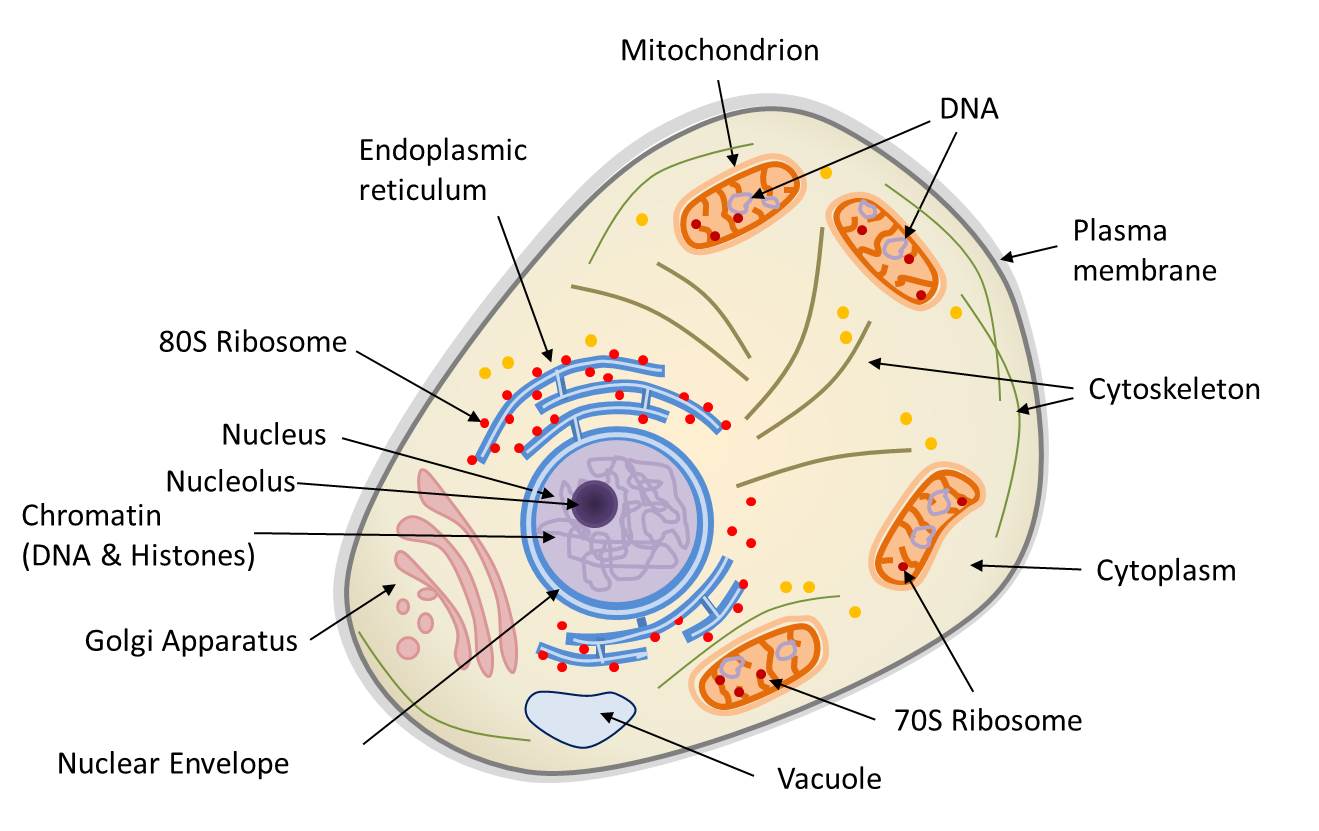
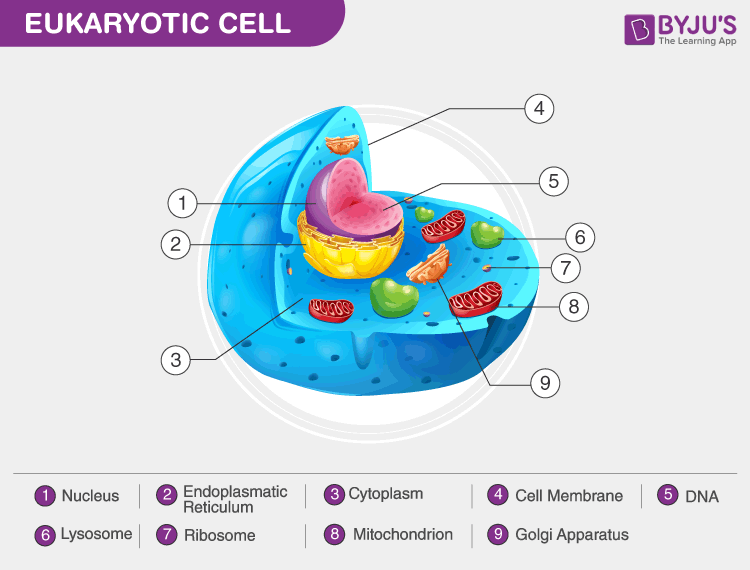
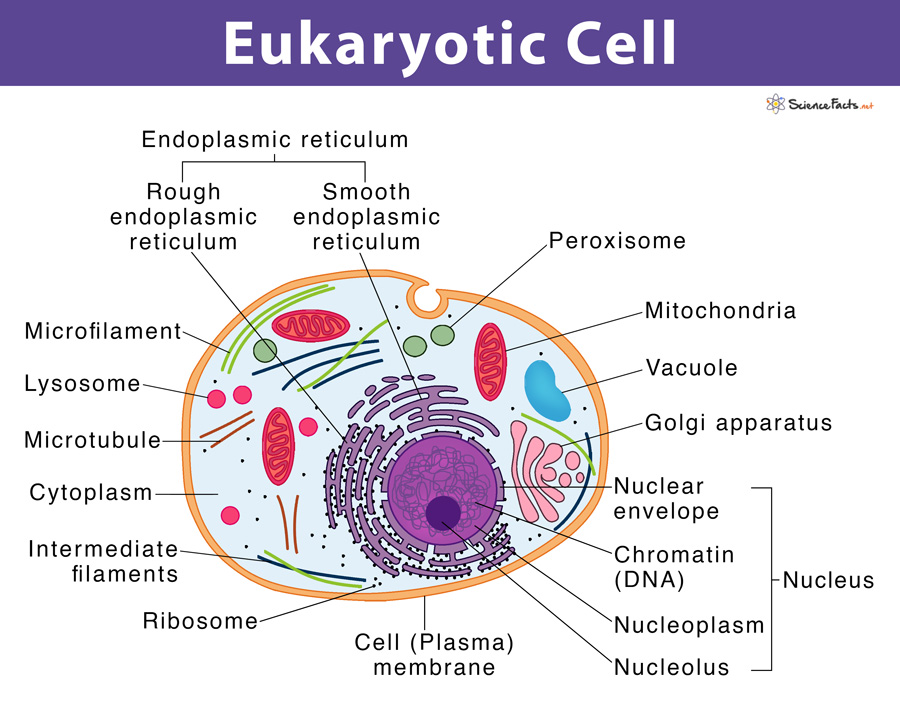
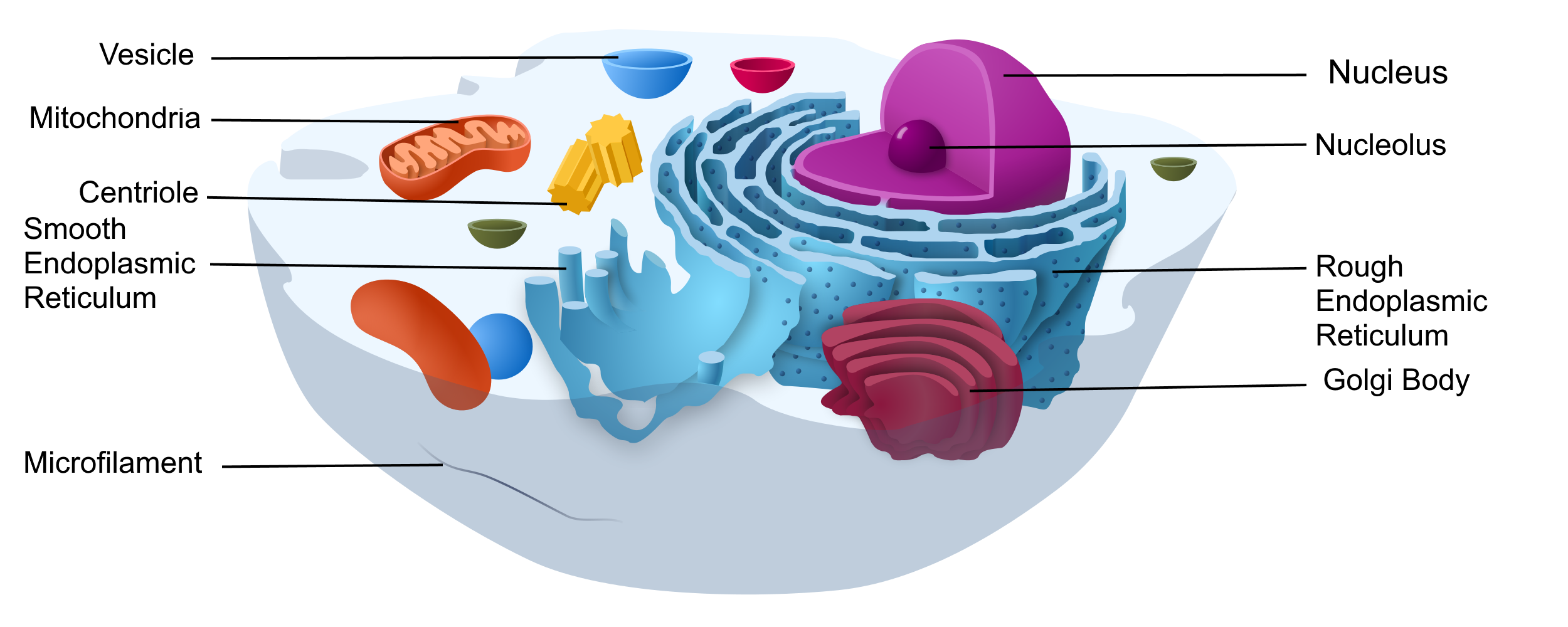
Eukaryotic Cell Drawing - Fungal and protist cells also have cell walls. Web how to draw eukaryotic cell/ step by step drawing for beginners eukaryotic cell, eukaryotic cell diagram, step by step drawing for beginners, biology diagram, diagrams, how to. Web key facts about eukaryotic cells; Web about press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright. The nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, cytoplasm, mitochondria, ribosomes, lysosomes are clearly mentioned in the diagram.
Web if you examine the diagram above depicting plant and animal cells, you will see in the diagram of a plant cell a structure external to the plasma membrane called the cell wall. Web eukaryotic cell diagram mentioned below depicts different cell organelles present in eukaryotic cells. Their size is significantly larger than prokaryotic cells, with an average of 10 to 100 µm in diameter. Except monera, the cells of all other kingdoms have eukaryotic organisation. The cell wall is a rigid covering that protects the cell, provides structural support, and gives shape to the cell. Describe the structure of eukaryotic plant and animal cells state the role of the plasma membrane summarize the functions of the major cell organelles describe the cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix Smallest functional unit within a living organism that can function independently:
Eukaryotic Cell Definition, Characteristics, Structure and Examples
Web eukaryotic cell diagram mentioned below depicts different cell organelles present in eukaryotic cells. The nucleus is surrounded by a complex nuclear membrane. Eukaryotic cells have mitochondria for cellular respiration. It is absent in animal cells and some protists. Because a membrane surrounds eukaryotic cell’s nucleus, it has a “true. Web the endoplasmic reticulum in.
1.4. Eucaryotic cell structure Biolulia European Sections
Hydrolytic enzymes, membrane and transport proteins. 2.3.2 annotate the diagram from 2.3.1 with the functions of each named structure. Web anatomy of the lysosome: Except monera, the cells of all other kingdoms have eukaryotic organisation. Web if you examine the diagram above depicting plant and animal cells, you will see in the diagram of a.
Symbiosis and evolution at the origin of the eukaryotic cell
Web unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: Web key facts about eukaryotic cells; Web learning objectives by the end of this section, you will be able to: The nucleus is surrounded by a complex nuclear membrane. Web there are two main types of cells, prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Web how to draw eukaryotic cell/ step by.
Diagram Of A Eukaryotic Cell Drivenheisenberg
Hydrolytic enzymes, membrane and transport proteins. Their size is significantly larger than prokaryotic cells, with an average of 10 to 100 µm in diameter. The nucleus is surrounded by a complex nuclear membrane. Dna is the genetic material of the eukaryotic cell. Vector diagram for medical use eukaryotic cell stock illustrations Ribosomes and lyosomes and.
3.4 Unique Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cells Microbiology 201
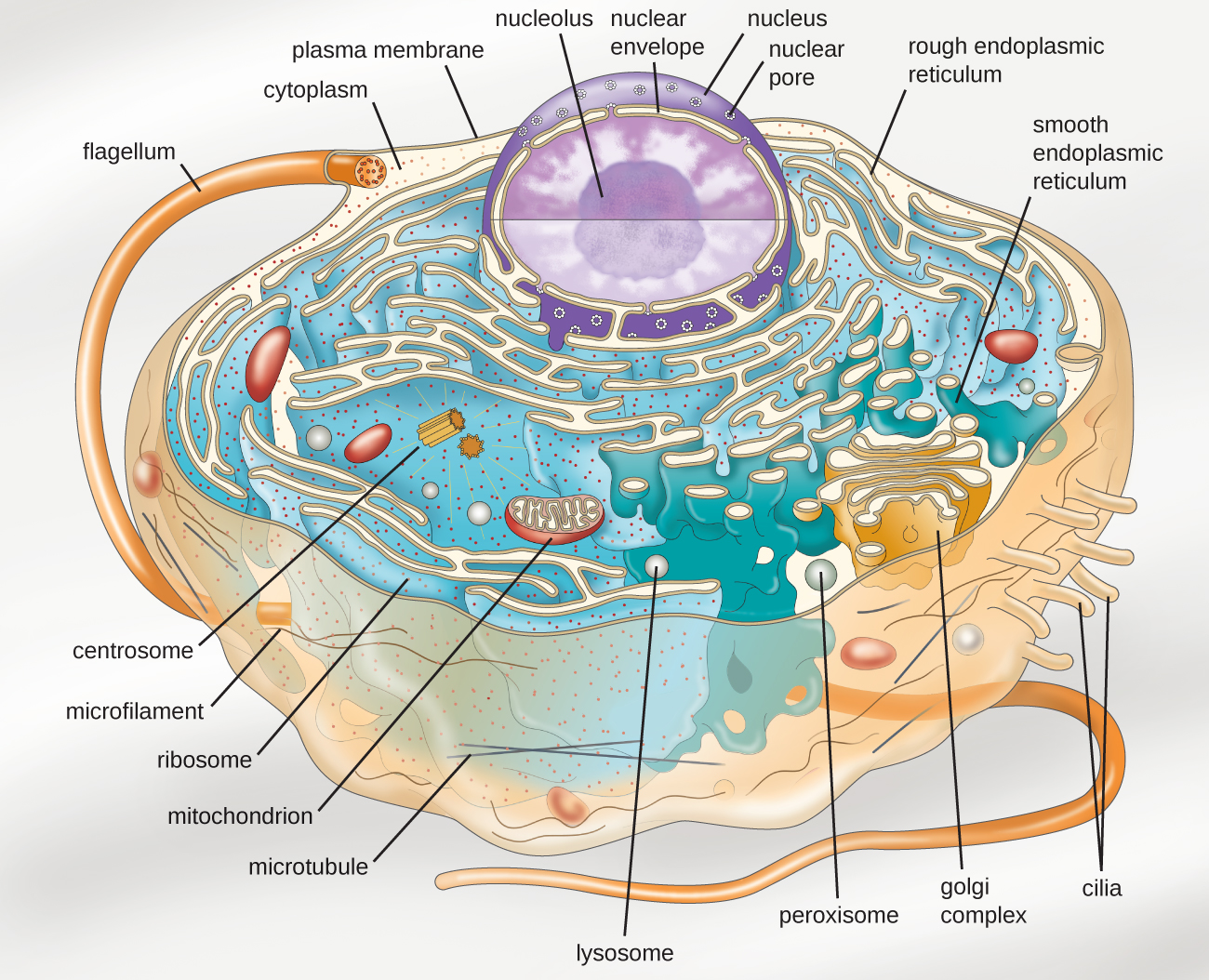
In figure 3.7b, the diagram of a plant cell, you see a structure external to the plasma membrane called the cell wall. This organelle use the enzymes to break down and digest food particles, engulfed viruses or bacteria in the cell. Web anatomy of the lysosome: It is absent in animal cells and some protists..
Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cellular Structures ALevel Biology
Web unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: Vector diagram for medical use eukaryotic cell stock illustrations Web if you examine the diagram above depicting plant and animal cells, you will see in the diagram of a plant cell a structure external to the plasma membrane called the cell wall. In figure 3.7b, the diagram of.
Eukaryotic Cells Definition, Characteristics, Structure, & Examples
They're also the more complex of the two. Because a membrane surrounds eukaryotic cell’s nucleus, it has a “true. Dna is the genetic material of the eukaryotic cell. Web how big are eukaryotic cells. The shape of eukaryotic cells varies significantly with the type of cell. Fungal and protist cells also have cell walls. The.
Eukaryotic Cell Definition, Structure, & Examples
The shape of eukaryotic cells varies significantly with the type of cell. The nucleus is surrounded by a complex nuclear membrane. Their size is significantly larger than prokaryotic cells, with an average of 10 to 100 µm in diameter. Cell wall is present in cells of plants, fungi and some protists. Hydrolytic enzymes, membrane and.
Biology 101 Cells Owlcation
Web eukaryotic cells 2.3.1 draw and label a diagram of the ultrastructure of a liver cell as an example of an animal cell. Cell wall is present in cells of plants, fungi and some protists. Fungal and protist cells also have cell walls. The only organisms that are not based on the eukaryotic cell are.
4.3 Variation in Cells Human Biology
Web key facts about eukaryotic cells; Fungal and protist cells also have cell walls. Hydrolytic enzymes, membrane and transport proteins. Hydrolytic enzymes, membrane and transport proteins. The cell wall is a rigid covering that protects the cell, provides structural support, and gives shape to the. Prokaryotes are cells that do not have membrane bound nuclei,.
Eukaryotic Cell Drawing The cell wall is a rigid covering that protects the cell, provides structural support, and gives shape to the. Web how big are eukaryotic cells. The nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, cytoplasm, mitochondria, ribosomes, lysosomes are clearly mentioned in the diagram. Web anatomy of the lysosome: Found either floating free in the cytoplasm or attached to the surface of the rough.
Web Key Facts About Eukaryotic Cells;
Web about press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright. Web how big are eukaryotic cells. Smallest functional unit within a living organism that can function independently: Wall less cells are generally irregular.
Because A Membrane Surrounds Eukaryotic Cell’s Nucleus, It Has A “True.
Their size is significantly larger than prokaryotic cells, with an average of 10 to 100 µm in diameter. Organisms that are based on the eukaryotic cell are called “eukaryotes” and include plants, animals, fungi, and protists. Web anatomy of the lysosome: This organelle use the enzymes to break down and digest food particles, engulfed viruses or bacteria in the cell.
Vector Diagram For Medical Use Eukaryotic Cell Stock Illustrations
Drawing eukaryotic cells and annotating the functions of each of the organelles. Eukaryotic cells have mitochondria for cellular respiration. Hydrolytic enzymes, membrane and transport proteins. Web a eukaryotic cell is one of two different types of cells.
Prokaryotes (Bacteria And Archaea) And Eukaryotic Cells (In Animals, Plants, Algae, And.
Web what exactly are eukaryotic cells? The cell wall is a rigid covering that protects the cell, provides structural support, and gives shape to the cell. The rest of our discussion will strictly be on eukaryotes. They're also the more complex of the two.