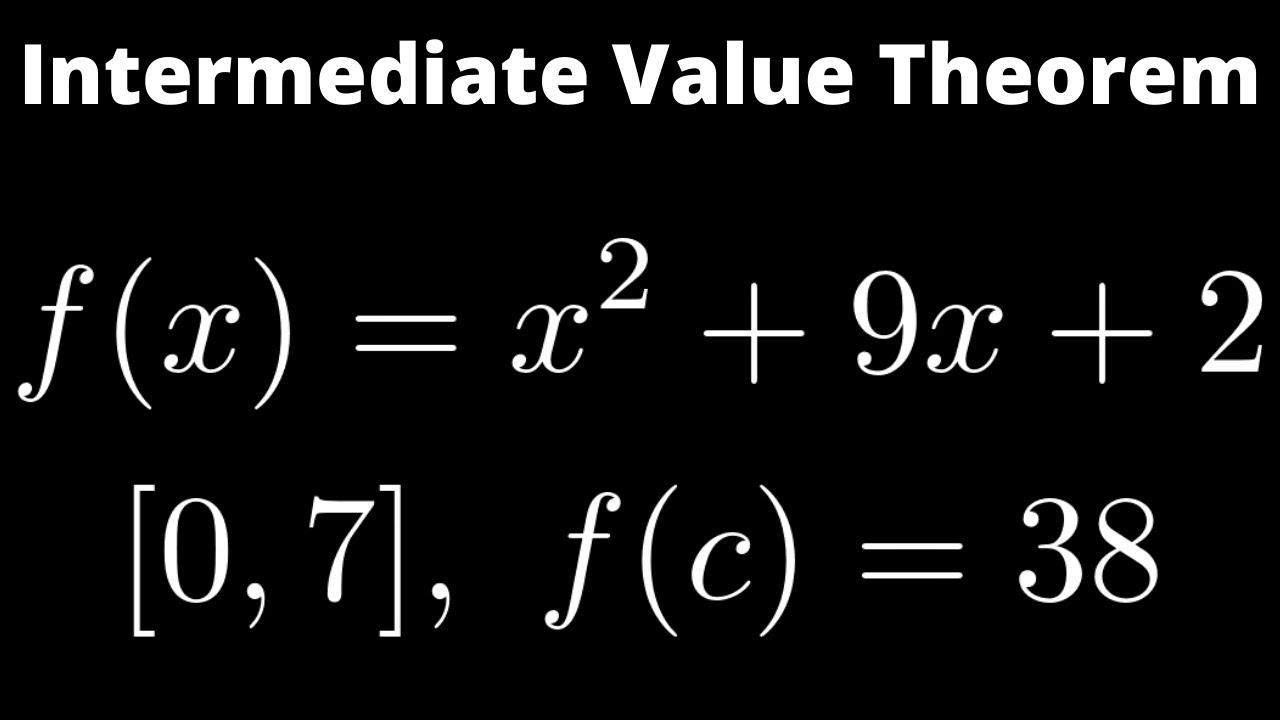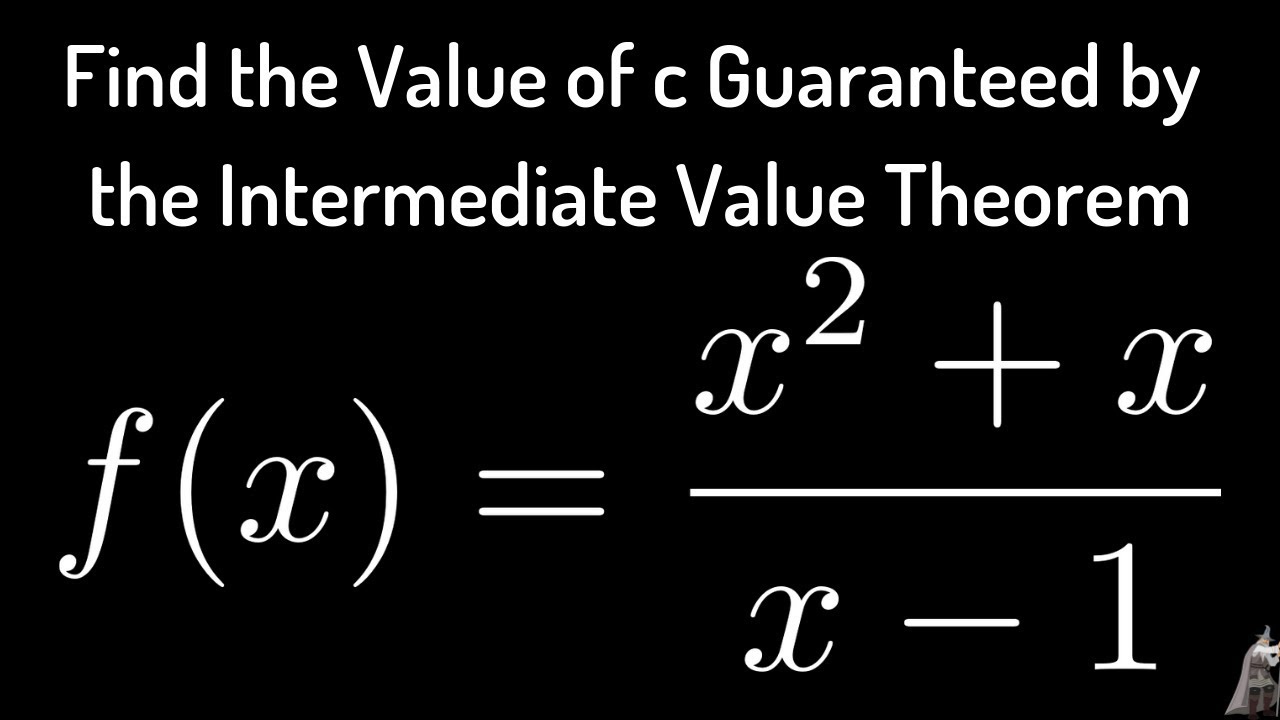Intermediate Value Calculator
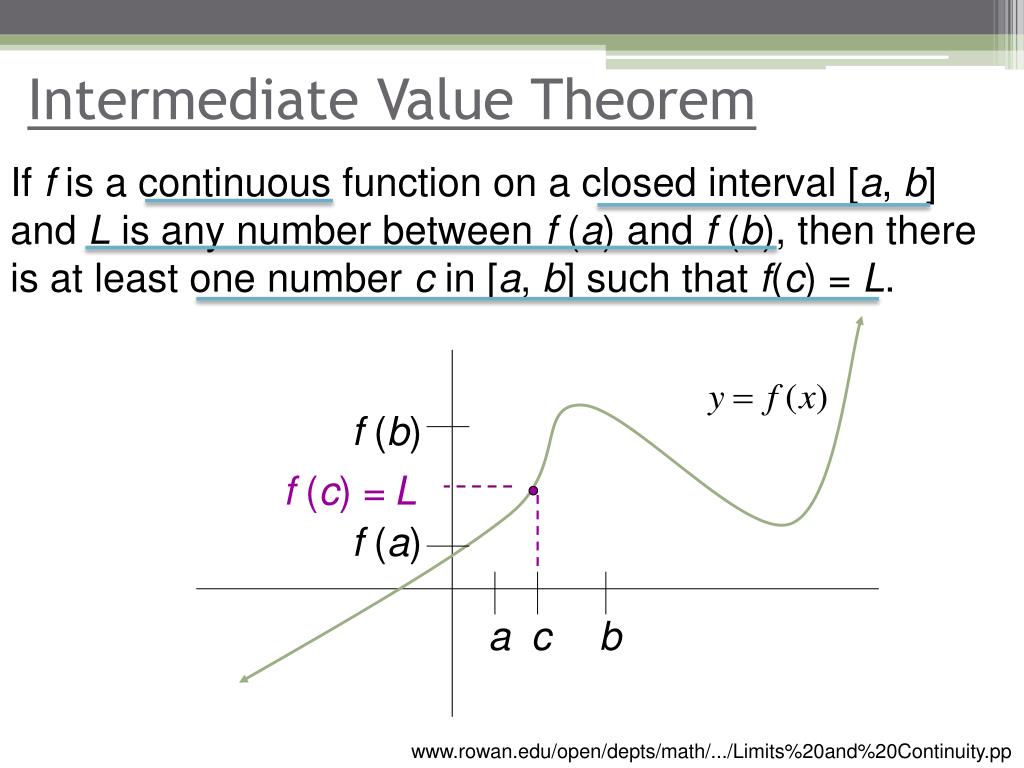
Intermediate Value Calculator - For any function f that's continuous over the interval [a, b] , the function will take any value. For a given continuous function f (x) in a given interval [a,b],. Web this method is based on the intermediate value theorem for continuous functions, which says that any continuous function f (x) in the interval [a,b] that satisfies f (a) * f (b) < 0. There is a point above some line and a point below that line, and that the curve is continuous, we can then safely say yes, there. Web discover the intermediate value theorem, a fundamental concept in calculus that states if a function is continuous over a closed interval [a, b], it encompasses every value between f (a) and f (b) within that range.
Web explore math with our beautiful, free online graphing calculator. Web how do you solve algebraic expressions? Web the intermediate value theorem. Whenever we can show that: Web intermediate value theorem:if a continuous function f with a closed interval [a,b] with points f(a) and f(b) then a point c exists where f(c) is between f(a) and f(b) 1 f x = x + 2 x. Graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more. Dive into this foundational theorem and.
Intermediate Value Theorem and Using TI83 TI84 Calculator to
Web discover the intermediate value theorem, a fundamental concept in calculus that states if a function is continuous over a closed interval [a, b], it encompasses every value between f (a) and f (b) within that range. Web intermediate value theorem:if a continuous function f with a closed interval [a,b] with points f(a) and f(b).
Calculus 2.7d Intermediate Value Theorem Examples YouTube
Web how is this useful? For a given continuous function f (x) in a given interval [a,b],. I.e., the converse of the. Web intermediate value theorem:if a continuous function f with a closed interval [a,b] with points f(a) and f(b) then a point c exists where f(c) is between f(a) and f(b) 1 f x.
The Intermediate Value Theorem Explained! Calculus YouTube
Web how do you solve algebraic expressions? I.e., the converse of the. Web the intermediate value theorem. Web intermediate value theorem:if a continuous function f with a closed interval [a,b] with points f(a) and f(b) then a point c exists where f(c) is between f(a) and f(b) 1 f x = x + 2 x..
Intermediate value theorem Example 2.mp4 YouTube
Web equations inequalities scientific calculator scientific notation arithmetics complex numbers polar/cartesian simultaneous equations system of inequalities polynomials. Web use the intermediate value theorem to show that the following equation has at least one real solution. For a given continuous function f (x) in a given interval [a,b],. For two real numbers \ (a\) and \.
PPT Intermediate Value Theorem PowerPoint Presentation, free download
For a given continuous function f (x) in a given interval [a,b],. The theorem basically sates that: If f is continuous on a closed interval [a,b], and c is any number between f(a) and f(b) inclusive, then there is at least one. For two real numbers \ (a\) and \ (b\) with \ (a <.
Find the Value of c Guaranteed by Intermediate Value Theorem for f(x
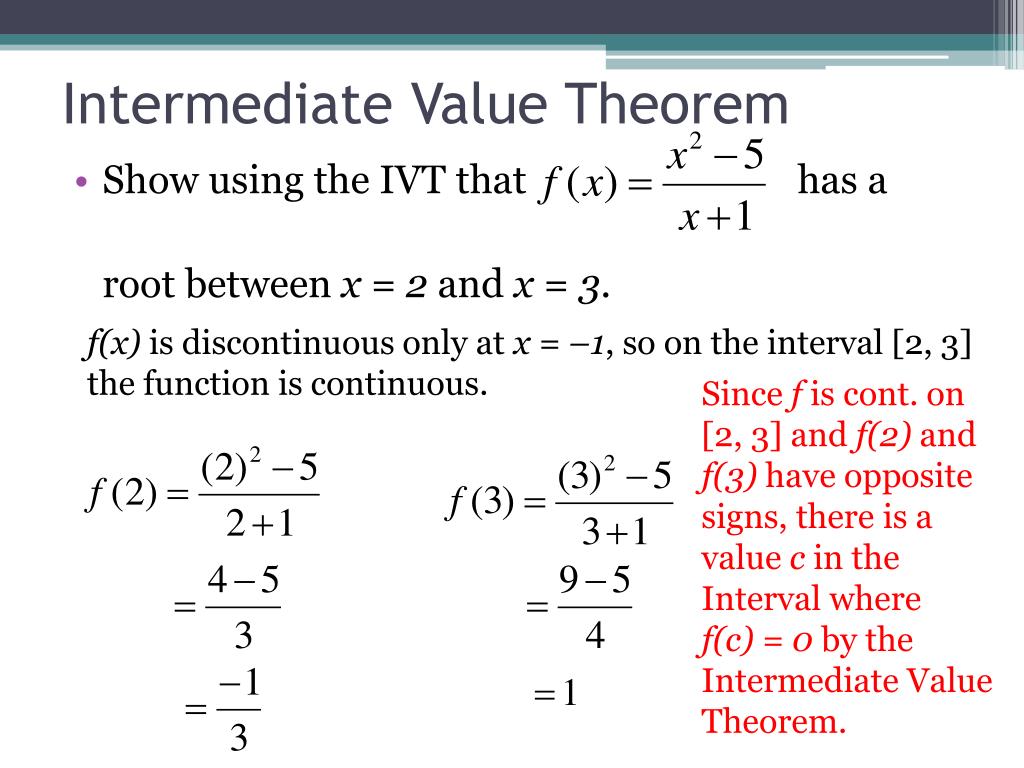
Web by the intermediate value theorem, \(f(0)\) and \(f(1)\) have the same sign; Graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more. Web use the intermediate value theorem to show that the following equation has at least one real solution. The intermediate value theorem states that there is a root f.
SOLUTION calculate INTERMEDIATE VALUE THEOREM Studypool
Web use the intermediate value theorem to show that the following equation has at least one real solution. Web the intermediate value theorem (ivt) in calculus states that if a function f (x) is continuous over an interval [a, b], then the function takes on every value between f (a) and f (b). The intermediate.
How to Find the Value of c in the Intermediate Value Theorem Quadratic
For two real numbers \ (a\) and \ (b\) with \ (a < b\), let \ (f\) be a continuous function on the closed interval \ ( [a, b].\) then for every \ (y_0\) between \ (f. For any function f that's continuous over the interval [a, b] , the function will take.
35+ Intermediate Value Theorem Calculator
Web how is this useful? The theorem basically sates that: Web by the intermediate value theorem, \(f(0)\) and \(f(1)\) have the same sign; If f is continuous on a closed interval [a,b], and c is any number between f(a) and f(b) inclusive, then there is at least one. Web how do you solve algebraic expressions?.
How to Find c in the Intermediate Value Theorem with f(x) = (x^2 + x
There is a point above some line and a point below that line, and that the curve is continuous, we can then safely say yes, there. For two real numbers \ (a\) and \ (b\) with \ (a < b\), let \ (f\) be a continuous function on the closed interval \ ( [a, b].\).
Intermediate Value Calculator Whenever we can show that: The intermediate value theorem states that there is a root f (c) = 0 f ( c) = 0 on the. Web to answer this question, we need to know what the intermediate value theorem says. Web this method is based on the intermediate value theorem for continuous functions, which says that any continuous function f (x) in the interval [a,b] that satisfies f (a) * f (b) < 0. I.e., the converse of the.
There Is A Point Above Some Line And A Point Below That Line, And That The Curve Is Continuous, We Can Then Safely Say Yes, There.
Web explore math with our beautiful, free online graphing calculator. The intermediate value theorem states that there is a root f (c) = 0 f ( c) = 0 on the. The theorem basically sates that: Web by the intermediate value theorem, \(f(0)\) and \(f(1)\) have the same sign;
Web This Method Is Based On The Intermediate Value Theorem For Continuous Functions, Which Says That Any Continuous Function F (X) In The Interval [A,B] That Satisfies F (A) * F (B) < 0.
Web intermediate value theorem:if a continuous function f with a closed interval [a,b] with points f(a) and f(b) then a point c exists where f(c) is between f(a) and f(b) 1 f x = x + 2 x. Web the intermediate value theorem (ivt) in calculus states that if a function f (x) is continuous over an interval [a, b], then the function takes on every value between f (a) and f (b). If f is continuous on a closed interval [a,b], and c is any number between f(a) and f(b) inclusive, then there is at least one. To solve an algebraic expression, simplify the expression by combining like terms, isolate the variable on one side of the equation by.
Intermediate Value Theorem Vs Mean Value Theorem.
Web the intermediate value theorem describes a key property of continuous functions: Web discover the intermediate value theorem, a fundamental concept in calculus that states if a function is continuous over a closed interval [a, b], it encompasses every value between f (a) and f (b) within that range. Web equations inequalities scientific calculator scientific notation arithmetics complex numbers polar/cartesian simultaneous equations system of inequalities polynomials. Web to answer this question, we need to know what the intermediate value theorem says.
For Any Function F That's Continuous Over The Interval [A, B] , The Function Will Take Any Value.
Dive into this foundational theorem and. For two real numbers \ (a\) and \ (b\) with \ (a < b\), let \ (f\) be a continuous function on the closed interval \ ( [a, b].\) then for every \ (y_0\) between \ (f. However, not every darboux function is continuous; Web the intermediate value theorem.