The cell theory, a fundamental concept in biology, is a cornerstone of our understanding of life and its intricate mechanisms. At its core, the cell theory posits that all living organisms are composed of one or more cells, that cells are the basic units of life, and that all cells arise from pre-existing cells. This theory, which has been refined over centuries through meticulous scientific observation and experimentation, underscores the cellular basis of life, emphasizing that cells are the smallest units of life that can replicate independently, and that all organisms, from the simplest bacteria to the most complex plants and animals, are either unicellular or multicellular.
To delve deeper into the cell theory, it’s essential to explore its three primary principles: 1. All Living Things Are Composed of One or More Cells: This principle asserts that cells are the fundamental building blocks of life. Every living organism, regardless of its complexity, is made up of cells. This includes bacteria, which are single-celled organisms, and humans, who are multicellular, with approximately 37.2 trillion cells in the average adult.
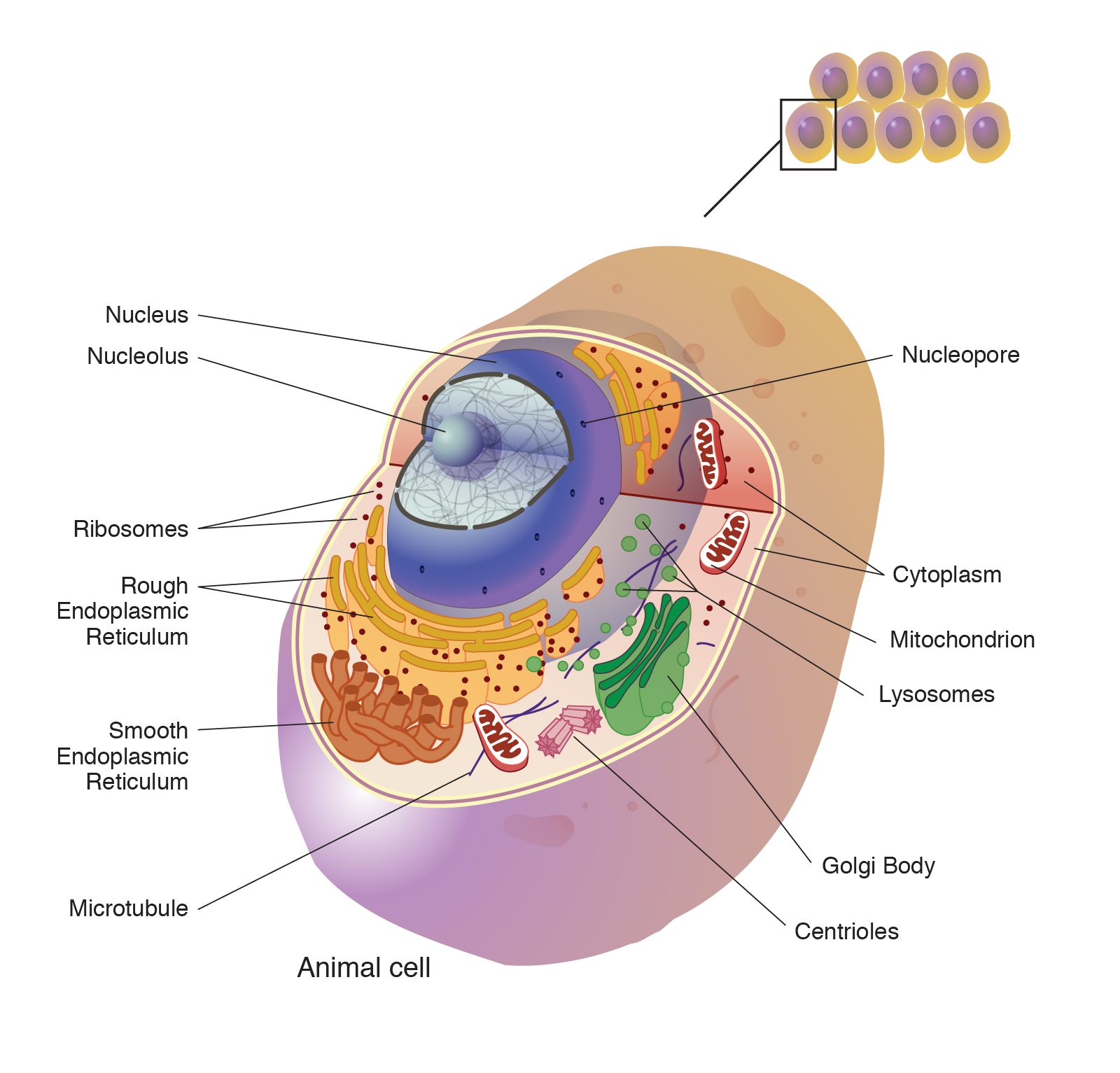
Cells Are the Basic Units of Life: This principle emphasizes that cells are not only the structural units of living organisms but also the functional units. All the necessary components for life, including the genetic material (DNA or RNA), metabolic pathways, and the machinery for protein synthesis, are found within cells. Essentially, cells are where the essence of life unfolds, with processes such as metabolism, reproduction, and response to stimuli occurring at the cellular level.
All Cells Arise from Pre-existing Cells: This principle, often referred to as biogenesis, states that new cells are generated from existing cells through cell division. This principle refutes the idea of spontaneous generation, which once suggested that living organisms could arise from non-living matter. Instead, the cell theory confirms that every cell originates from a pre-existing cell, reinforcing the continuity of life.
Understanding the cell theory is crucial for grasping various biological phenomena, including growth, reproduction, and evolution. For instance, the process of cell division, whether mitosis in somatic cells or meiosis in reproductive cells, is fundamental to the propagation of life. Furthermore, the cell theory lays the groundwork for understanding diseases at a cellular level, such as cancer, which involves uncontrolled cell division, and genetic disorders, which can stem from mutations in the DNA within cells.
In addition to its foundational role in biology, the cell theory has significant implications for various fields, including medicine, biotechnology, and ecology. In medicine, understanding cell biology is critical for developing treatments and therapies, such as stem cell therapy, which aims to repair or replace damaged cells. In biotechnology, cell culture techniques are used to produce vaccines, hormones, and other biological products. In ecology, the cell theory helps explain how organisms interact with their environments at the cellular level, which is essential for understanding ecosystem dynamics and the impact of environmental changes on living organisms.
The historical development of the cell theory is also noteworthy, as it reflects the scientific community’s evolving understanding of life. The discovery of cells by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in the 17th century, followed by the formulation of the cell theory by Matthias Jakob Schleiden and Theodor Schwann in the 19th century, marked significant milestones. Since then, advances in microscopy, genetics, and molecular biology have further refined our understanding of cells and their role in life.
In conclusion, the cell theory is a comprehensive framework that underpins our understanding of biology and life. It not only explains the structure and function of living organisms at the most basic level but also provides insights into the mechanisms of life, from the simplest to the most complex. As scientific knowledge continues to evolve, the cell theory remains a foundational concept, guiding research, understanding, and application in biology and its allied fields.
To further explore the implications of the cell theory, let’s examine some of the key areas where it has a significant impact: - Medical Research and Practice: Understanding cell biology is crucial for developing new medical treatments. For instance, targeted therapies that focus on specific cellular pathways have revolutionized the treatment of diseases such as cancer. - Biotechnology: The cell theory underpins many biotechnological applications, including the production of vaccines, hormones, and other biological products through cell culture techniques. - Ecology and Environmental Science: Recognizing the cellular basis of life helps us understand how organisms interact with their environments and how environmental changes can impact ecosystems at the cellular level.
Given the cell theory’s central role in biology, it’s essential to continue exploring and refining our understanding of cells and their functions. This includes advancing our knowledge of cellular mechanisms, exploring the diversity of cellular life, and applying this knowledge to address global challenges in health, environment, and technology.
What is the primary assertion of the cell theory?
+The primary assertion of the cell theory is that all living organisms are composed of one or more cells, that cells are the basic units of life, and that all cells arise from pre-existing cells.
Why is the cell theory important in biology and medicine?
+The cell theory is crucial for understanding the basis of life and disease. It underpins medical research, the development of new treatments, and our comprehension of how organisms interact with their environments.
What are some of the key implications of the cell theory for biotechnology and ecology?
+The cell theory has significant implications for biotechnology, as it forms the basis for cell culture techniques used in the production of biological products. In ecology, it helps explain how environmental changes affect organisms at the cellular level, which is essential for understanding ecosystem dynamics.
In exploring the cell theory and its implications, we delve into the essence of life itself, revealing the intricate and fascinating world of cells that underlies all living organisms. By continuing to advance our understanding of cells and their functions, we open pathways to new discoveries, innovative technologies, and a deeper appreciation of the complex, interconnected world of life on Earth.