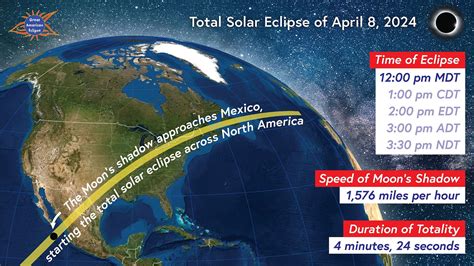
The awe-inspiring phenomenon of a total solar eclipse has captivated human imagination for centuries. This rare and breathtaking event occurs when the Moon passes directly between the Earth and the Sun, blocking the Sun’s light and casting a shadow on the Earth. For those eager to witness this spectacle, a total eclipse calendar is an indispensable tool.
To understand the frequency and occurrence of total solar eclipses, it’s essential to delve into the celestial mechanics behind this phenomenon. The Moon’s orbit is tilted at an angle of about 5 degrees with respect to the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. As a result, the Moon’s shadow usually falls above or below the Earth. However, when the Moon is in the right position, its shadow has two parts: the umbra, which is the darker inner shadow where the Sun is completely blocked, and the penumbra, which is the lighter outer shadow where the Sun is only partially blocked.
Total solar eclipses are relatively rare because the Earth, Moon, and Sun must be aligned in a straight line, a phenomenon known as syzygy. This alignment can only occur during a new moon, when the Moon is between the Earth and the Sun. Furthermore, the Earth, Moon, and Sun must also be aligned in the same plane, known as the ecliptic, to produce a total solar eclipse.
The path of totality, where the eclipse is visible in its entirety, is usually about 100 miles wide and covers a specific region on the Earth’s surface. This path is different for each eclipse and is determined by the Moon’s shadow on the Earth. Outside of this path, the eclipse is partial, and the Sun appears to be only partially covered by the Moon.
For eclipse enthusiasts and scientists alike, planning and preparation are key to witnessing and studying these events. A total eclipse calendar provides crucial information on the timing, location, and other details of upcoming eclipses. This includes the date, time, and duration of the eclipse, as well as the path of totality and any special viewing considerations.
The frequency of total solar eclipses is approximately once every 18 months on average, but most of these events are only visible from remote or oceanic areas. About once a year, a partial solar eclipse is visible from some part of the Earth, but total solar eclipses visible from land are much rarer, occurring about twice a decade on average.
In the era of advanced technology and global connectivity, following a total eclipse calendar has become easier than ever. With precise astronomical calculations and real-time updates, enthusiasts can plan their eclipse-watching adventures well in advance. Whether for scientific research, personal fascination, or the sheer thrill of witnessing a rare celestial event, understanding and utilizing a total eclipse calendar is essential for making the most of these extraordinary occurrences.
Total Eclipse Predictions and Planning
Predicting the path of totality and other details of a total solar eclipse involves intricate astronomical calculations. These predictions are based on the Moon’s elliptical orbit and the tilt of its orbit with respect to the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. The path of totality can shift due to the Moon’s slightly elliptical orbit, which causes its distance from the Earth to vary.
Planning an eclipse-watching trip requires careful consideration of several factors, including the weather, accessibility of the viewing location, and safety precautions. Viewing a total solar eclipse requires special solar viewing glasses or handheld solar viewers that meet international safety standards for solar viewers.
The Science Behind Total Solar Eclipses
Total solar eclipses offer a unique opportunity for scientists to study the Sun’s corona, the outer atmosphere of the Sun that is usually invisible because of the bright light of the Sun’s surface. During a total solar eclipse, the Moon blocks the direct light from the Sun, allowing the corona to be visible. This reveals intricate details about the Sun’s magnetic field and the temperature of the corona, which is millions of degrees hotter than the Sun’s surface.
The study of total solar eclipses also contributes to our understanding of the Earth’s climate. By observing the effects of the sudden drop in temperature during an eclipse, scientists can gain insights into the Earth’s energy balance and how the atmosphere responds to changes in solar radiation.
Witnessing a Total Solar Eclipse: Safety and Viewing Tips
Witnessing a total solar eclipse is a once-in-a-lifetime experience for many people. However, it’s crucial to prioritize eye safety during the event. Looking directly at the Sun during any phase of an eclipse without proper eye protection can cause serious eye damage, including solar retinopathy.
To safely view a total solar eclipse, one should use NASA-approved solar viewing glasses or handheld solar viewers. These devices have special filters that block out 99.999% of both UVA and UVB radiation and reduce the Sun’s intensity to a safe level for viewing.
It’s also important to check the weather forecast for the viewing location, as clear skies are essential for viewing the eclipse. Finally, finding a location within the path of totality is critical for witnessing the eclipse in its entirety.
Conclusion
Total solar eclipses are awe-inspiring natural phenomena that offer a glimpse into the celestial mechanics of our solar system. With the aid of a total eclipse calendar, enthusiasts and scientists can plan and prepare for these rare events, ensuring a safe and unforgettable viewing experience. Whether for personal fascination or scientific inquiry, the study and observation of total solar eclipses continue to captivate and inspire humanity.
How often do total solar eclipses occur?
+Total solar eclipses are relatively rare, occurring approximately once every 18 months on average, but most are only visible from remote or oceanic areas. Visible from land, they occur about twice a decade.
What is the path of totality during a total solar eclipse?
+The path of totality is the region on the Earth's surface where the eclipse is visible in its entirety. It is usually about 100 miles wide and is determined by the Moon's shadow on the Earth.
How can I safely view a total solar eclipse?
+To safely view a total solar eclipse, use NASA-approved solar viewing glasses or handheld solar viewers that block out 99.999% of both UVA and UVB radiation. Never look directly at the Sun without proper eye protection.
What scientific opportunities are presented by total solar eclipses?
+Total solar eclipses offer unique opportunities to study the Sun's corona, the Earth's climate, and the effects of the eclipse on the environment. They also allow for the observation of the Sun's magnetic field and the temperature of the corona.
How can I plan to witness a total solar eclipse?
+Use a total eclipse calendar to find upcoming eclipses and their paths of totality. Plan your viewing location, ensuring it is within the path of totality, and check the weather forecast. Always prioritize eye safety with proper viewing equipment.
As the world continues to marvel at the spectacle of total solar eclipses, the importance of accurate information, safety precautions, and a deep understanding of the celestial phenomena involved cannot be overstated. Whether you are an avid astronomer, a curious observer, or simply someone fascinated by the wonders of the universe, embracing the knowledge and awe inspired by total solar eclipses can enrich your perspective and foster a deeper connection to the cosmos.